Статья опубликована на с. 71-79
Введение
Головная боль напряжения (ГБН) является самой частой формой первичной ГБ. Распространенность ГБН в течение жизни в общей популяции, по различным данным, варьирует от 30 до 78 %, что значительно превышает распространенность мигрени. Редкие эпизоды ГБН, возникающие с частотой один или два раза в год, вряд ли расцениваются как заболевание и не учитываются в эпидемиологических исследованиях. Хотя нечастые ГБН (1 и менее раз в месяц) имеют очень высокую распространенность в популяции (51–59 %), они не являются поводом для обращения к специалистам. На практике лица, испытывающие редкие ГБН, не расцениваются как потенциальные пациенты. Между тем от 18 до 37 % людей в популяции страдают ГБН с частотой более 1 раза в месяц, 10–20 % — еженедельными приступами, и 2–6 % популяции имеют ХГБН длительностью более полугода [1]. ГБ, обычно двусторонняя и умеренной интенсивности, имеет сжимающий или давящий непульсирующий характер, часто по типу «обруча» или «каски», может появляться вскоре после пробуждения, и присутствует на протяжении всего дня, то усиливаясь, то ослабевая. Характерно возникновение или усиление боли на фоне эмоционального напряжения и ее облегчение в состоянии психологического расслабления. В отличие от мигрени головная боль при ГБН чаще является двусторонней, имеет легкую или умеренную интенсивность, обычно не сопровождается тошнотой и рвотой, но при ней может снижаться аппетит; иногда боли может сопутствовать умеренно выраженная чувствительность к свету или звукам; во время эпизода ГБН пациенты сохраняют способность работать и выполнять свои обычные обязанности [2].
Клинически ГБН характеризуется своеобразным ноцицептивным рисунком в виде монотонной, тупой, давящей, стягивающей, ноющей боли; практически не бывает боли пульсирующего характера. Довольно часто пациенты предъявляют жалобы не столько на боль, сколько на чувство сдавления или сжимания головы, наличие скованности в виде «каски», «шлема», «ленты, натянутой вокруг головы». В отличие от мигрени ГБН не имеет четкой локализации. Она, как правило, двусторонняя, с эпицентром в области лба, затылка или темени. Может отмечаться лобно-теменная, лобно-височная или затылочно-шейная локализация с иррадиацией в оба виска, лицо, плечи, сопровождающаяся чувством давления на глазные яблоки. Эти ощущения усиливаются от ношения плотного головного убора [3]. По данным [3], выделяют следующие клинические признаки головной боли напряжения:
Локализация боли: чаще двусторонняя, диффузная, иногда с преобладанием в лобно-теменных, лобно-височных, затылочно-теменных отделах.
Характер боли: монотонный, стягивающий по типу «каски», «шлема», «обруча».
Интенсивность боли: умеренная, реже выраженная, но обычно не меняющаяся при повседневной физической нагрузке.
Длительность болевых ощущений: при эпизодической форме длительность одного приступа от 30 минут до 7 дней, при этом количество дней с головной болью не превышает 15 в месяц (менее 180 в год); при хронической число эпизодов ГБ более 15 дней в месяц или свыше 180 дней в году.
Сопровождающие симптомы: тошнота, редко фото-, фонофобия, снижение аппетита, вплоть до анорексии, алгические проявления (кардиалгии, абдоминальные боли и др.).
Нарушения эмоционально-личностной сферы: повышенная возбудимость, тревога, депрессия, демонстративные проявления, ипохондрический синдром.
Классификация ГБН. ГБН является официально признанной нозологической единицей, в МКБ‑10 она находится в рубрике G44.2 [4, 5].
Наличие у пациента ГБН можно установить, если головная боль имеет следующие характеристики (как минимум две из нижеперечисленных):
— двусторонняя локализация;
— сжимающий/давящий (непульсирующий) характер;
— интенсивность боли от легкой до умеренной;
— головная боль не усиливается от обычной физической нагрузки (например, ходьба, подъем по лестнице) [5].
ГБН как нозологическая форма диагностируется при отсутствии признаков другого заболевания, которое может сопровождаться головной болью, или если другие заболевания имеются, то ГБН не связана с ними по времени возникновения (то есть исключается вторичность головной боли).
В Международной классификации головных болей второго пересмотра [4, 5] ГБН подразделяется на несколько категорий:
2.1. Нечастая эпизодическая ГБН.
2.2. Частая эпизодическая ГБН.
2.3. Хроническая ГБН.
Каждая из этих категорий подразделяется на два подтипа: ГБН, сочетающаяся с напряжением перикраниальных мышц, и ГБН, не сочетающаяся с напряжением перикраниальных мышц. Основой для такого деления являются данные ЭМГ, альгометрии и пальпаторного исследования [6, 7]. Пальпаторное обнаружение мышечной болезненности является наиболее чувствительным и диагностически точным методом выявления напряжения перикраниальных мышц у больных ГНБ. В связи с этим в МКГБ‑2 для дифференциальной диагностики подтипов с напряжением и без напряжения мышц предлагается только метод пальпации (с надавливанием на различные перикраниальные мышцы). Чувствительность перикраниальных мышц легко выявляется при пальпации мелкими вращательными движениями вторым и третьим пальцами, а также при надавливании (желательно с помощью прессорного альгометра) в области лобных, височных, жевательных, крылонебных, грудино-ключично-сосцевидных и трапециевидных мышц. Чтобы получить общий балл болезненности (total tenderness score) для каждого пациента, необходимо суммировать баллы локальной болезненности, полученные при пальпации каждой отдельной мышцы и рассчитанные с помощью вербальной шкалы от 0 до 3 баллов. Клиническая практика подтвердила надежность и воспроизводимость пальпаторного метода с надавливанием на мышцы [7].
Для постановки нозологического диагноза «эпизодическая ГБН» необходимо соответствие клинической картины и анамнеза следующим критериям МКГБ‑2 [5].
1. Наличие в анамнезе не менее 10 приступов головной боли, соответствующих критериям ГБН. Число дней с такой головной болью должно составлять менее 15 в месяц (менее 180 в году).
2. Длительность головной боли от 30 минут до 7 дней.
В свою очередь, эпизодическая головная боль разделяется на нечастую и частую.
Нечастая эпизодическая головная боль напряжения (диагностические критерии) [5]:
А. По меньшей мере 10 эпизодов, возникающих с частотой не более 1 дня в месяц (не более 12 дней в год) и отвечающих критериям ГБН.
Б. Продолжительность головной боли от 30 минут до 7 дней.
Частая эпизодическая головная боль напряжения (диагностические критерии) [5]:
А. По меньшей мере 10 эпизодов, возникающих с частотой от 1 до 15 дней в месяц (от 12 до 180 дней в год) и отвечающих критериям ГБН.
Б. Продолжительность головной боли от 30 минут до 7 дней.
Частая ГБН нередко сочетается с мигренью без ауры. Наличие эпизодов ГБН у пациента с мигренью может быть выявлено с помощью дневника головной боли. Учитывая, что лечебные подходы при мигрени и ГБН существенно различаются, следует обучить пациентов различать эти два типа головной боли и применять соответствующую для каждого типа тактику лечения, чтобы избежать лекарственного абузуса [8].
Хроническая головная боль напряжения
Хроническая головная боль напряжения — расстройство, происходящее из эпизодической ГБН и проявляющееся очень частыми или ежедневными эпизодами головной боли продолжительностью от нескольких минут до нескольких суток [5].
Диагноз «хроническая ГБН» выставляется при наличии приступов головной боли, соответствующих приведенным выше критериям ГБН и длящихся более 15 дней в месяц (или более 180 дней в году) при общей длительности заболевания не менее 3 мес. [5].
Следует подчеркнуть, что диагноз «хроническая ГБН» используется в том случае, если хроническая ГБН происходит из эпизодической ГБН (т.е. когда с течением времени эпизодическая ГБН переходит в хроническую ГБН). В том случае, когда критерии ГБН выполняются, но головная боль изначально не имеет ремиссий (т.е. приобретает хронический характер в течение первых 3 дней после появления боли), такую головную боль следует отнести к другим первичным, а именно к «новой ежедневно (изначально) персистирующей головной боли» [6].
Патогенез ГБН
В данное время нет единого взгляда на патогенез ГБН. Многочисленные теории возникновения ГБН периодически расходятся в определении доминантности тех или иных механизмов развития данной патологии. В происхождении ГБН принимают участие как периферические, так и центральные ноцицептивные механизмы; среди последних — снижение активности антиноцицептивной системы, в частности недостаточность ингибиторных механизмов ствола мозга [9]. Механизмы формирования эпизодических и хронических ГБН, по современным данным, принципиально различаются. При ЭГБН первоочередное значение приобретают периферические (мышечные) факторы, тогда как при ХГБН патогенетические механизмы носят мультифакторный характер. Но у большинства пациентов с ХГБН имеют значение как периферические, так и центральные факторы [10]. В происхождении фактора мышечного напряжения при ГБН в целом может иметь значение периферическая сенситизация миофасциальных ноцицепторов как результат высвобождения провоспалительных пептидов. В происхождении ХГБН особая роль отводится механизмам центральной сенситизации, что отличает ее от ЭГБН, при которой болевая перцепция в целом не отличается от нормы [1]. Также в патогенезе ГБН существенное значение приобретает наличие хронического эмоционального стресса, который формируется под влиянием индивидуально значимых психогенных факторов у лиц с определенными особенностями личности и недостаточностью механизмов психологической защиты, а также функциональной недостаточностью антиноцицептивных систем. Указанные нарушения приводят к возникновению вегетативно-эндокринной и психомоторной активации, что проявляется повышением мышечного тонуса, ишемией, отеком и биохимическими проявлениями в мышечной ткани [9]. На формирование ГБН существенное влияние оказывают невротические особенности личности и наличие хронического стресса, что приводит к нарушению функционального состояния лимбико-ретикулярного комплекса [7]. Это сопровождается изменениями в действии ноци- и антиноцицептивной системы, развитием тревожно-депрессивного синдрома и нарушением функционального состояния системы «тройничный — лицевой нервы». В результате возникает гипертонус и гипоксия перикраниальных и мимических мышц, что клинически выражается появлением ГБ [3]. Некоторые авторы связывают возникновение ГБН с мышечно-тоническим синдромом (МТС). В основе формирования МТС лежит механизм порочного круга, когда повторяющееся напряжение мышцы, возникающее в ответ на эмоциональный стресс, приводит к ее рефлекторному напряжению (спазму). В результате повышается возбудимость ноцицептивных нейронов в структурах ЦНС, в том числе мотонейронов передних рогов спинного мозга; длительное тоническое напряжение приводит к гипоксии мышцы, ее воспалению, позднее формируется вторичная гипералгезия, усиливающая мышечный спазм и приводящая к хронизации боли [10]. Предполагается, что в происхождении нечастой и частой ЭГБН принимают участие периферические, а при хронической ГБН — центральные ноцицептивные механизмы. ГБН с напряжением перикраниальных мышц имеет в своей патофизиологической основе механизм мышечного напряжения.
Напряжение мышц, в свою очередь, может развиваться двумя путями. Первый путь — центральный — нарушение интегративной функции лимбико-ретикулярных структур, проявляющееся повышенной тревожностью, симпатоадреналовой активацией, которая, в свою очередь, сопровождается повышением нервно-мышечной возбудимости. При этом механизме причина головной боли лежит в дисбалансе центральных систем, регулирующих психофизиологические реакции и соотношение ноцицептивной и антиноцицептивной системы [10]. Центральные расстройства носят первичный характер, а напряжение перикраниальных мышц определяет вторичную периферическую сенсорную составляющую — сжимающую и сдавливающую головную боль. Вторым механизмом ГБН с дисфункцией перикраниальных мышц является периферический — перенапряжение перикраниальных мышц с формированием триггерных точек. У таких больных пальпаторно или с помощью прессорного альгометра определяется повышенная чувствительность (болезненность) мышц скальпа, а электромиографическое исследование позволяет выявить повышенную активность перикраниальных мышц [6, 10].
Клинически мышечная дисфункция у пациентов с первичной ГБ проявляется преходящими или постоянными болевыми ощущениями и/или чувством напряжения и дискомфорта в области затылка, задней поверхности шеи и надплечий (зона «вешалки для пальто»), которые усиливаются при длительном позном напряжении, во время эмоциональных переживаний, нередко в положении лежа. Жалобы на болезненность и напряжение мышц нарастают по мере увеличения интенсивности и частоты эпизодов ГБ, а также по мере увеличения силы боли во время самого эпизода [7].
ГБН без вовлечения (напряжения) перикраниальных мышц по клиническим характеристикам мало отличается от ГБН с вовлечением перикраниальных мышц, но не сопровождается повышением электрической активности на ЭМГ. При этом пальпация перикраниальных тканей оказывается болезненной, что может свидетельствовать о снижении порога болевой чувствительности рецепторов в структурах перикраниальных тканей [2]. В данном случае периферическим патогенетическим звеном являются не только мышцы, но и сухожильный апоневроз или кожа и подкожная клетчатка. Данный механизм ГБН основан на нарушении соотношения ноцицептивно-антиноцицептивных механизмов и нейротрансмиттерном дисбалансе и сопровождается снижением порога болевой чувствительности. У пациентов данной клинической группы, как правило, проявляются тревожно-депрессивные нарушения [6]. Указанные процессы приводят к усилению боли и мышечной активности (повышение спонтанной активности перикраниальных и шейных мышц, наличие отдаленных синергий). Таким образом, нарушаются и психомоторные соотношения, обусловливая возникновение порочного круга. Наличие тревожно-депрессивных расстройств и дисфункция лимбико-ретикулярного комплекса с дисрегуляцией ноцицептивных систем приводят к нарушению психомоторных соотношений, усиливающих дезинтеграцию деятельности лимбико-стволовых структур и в конечном итоге обусловливающих возникновение ГБН [9, 10].
Сосудистые механизмы ГБН
Вопрос роли сосудистых механизмов в развитии ГБН остается актуальным на протяжении ряда лет. В ряде исследований [3, 9, 11, 12] приводятся данные о наличии мышечной и сосудистой гипертонии при ГБН, что может быть связано с гиперсимпатикотонией. Предполагается, что повышенная концентрация калия, возникающая во время длительного напряжения мышцы, стимулирует ее хеморецепторы и вызывает боль. Кроме того, у этих больных возникает спонтанное снижение пульсового кровотока, т.е. черепные артерии находятся в состоянии сужения. В других исследованиях [13] показано, что повышение напряжения мышц приводит к сужению артериальных сосудов и появлению ишемии. Сужение малых артерий, питающих мышцы, вызывает соответствующую степень венозного застоя, и таким образом формируется порочный круг. Мышца недостаточно снабжается кровью, а вследствие усиления напряжения в ней накапливаются продукты метаболизма, которые не могут быть в соответствующей степени выведены через венозную сеть. При этом мышца становится отечной и болезненной. Выделяют два параллельных патогенетических механизма, вызывающих боль при напряжении мышц [3, 12]:
— напряжение самих мышц, ишемия, отек и химические изменения в них;
— конкурентное сужение артерий, еще более ухудшающее ситуацию.
Современные исследования показывают влияние различных структур и функциональных систем головного мозга на механизмы развития ГБН. Основными интракраниальными источниками головной боли являются участки твердой мозговой оболочки (основание черепа, стенки больших венозных синусов), артерии основания мозга, внечерепные артерии, которые иннервируются 1-й ветвью тройничного нерва. Длительное болевое раздражение со стороны внутримозговых сосудов (преимущественно венозных) может спровоцировать напряжение трапециевидных и грудино-ключично-сосцевидных мышц, контролируемых моторными нейронами передних рогов С1-С3 сегментов спинного мозга и ядром добавочного нерва, и вызвать развитие ГБН посредством переключения с ядра спинномозгового пути тройничного нерва на вышеуказанные ядра [14]. В процессе хронизации ГБН играет роль сенситизация центральной нервной системы к длительной болевой импульсации и недостаточность антиноцицептивный системы [15]. Исходя из представлений недостаточности норадренергической и серотонинергической систем у больных с хронической болью, можно предположить вторичное влияние медиаторных механизмов на системную гемодинамику, и в частности мозговой кровоток. Длительный стресс приводит к увеличению мозгового метаболизма и, следовательно, к увеличению артериального притока, который, в свою очередь, требует адекватного венозного оттока. Органическое или функциональное нарушение венозного оттока может приводить к переполнению венозных синусов и раздражению тройничного нерва [9]. Таким образом, нарушение взаимоотношения между артериальной и венозной системами кровообращения головного мозга может быть одним из факторов, приводящих к возникновению и хронизации головной боли. Проведенные исследования показали значение сосудистого механизма как одного из ведущих патогенетических факторов как при первичных ГБН, так и при вторичных ее формах (ГБ при артериальной гипертензии, патологии венозных синусов твердой мозговой оболочки и аномалии Киари I типа) [14].
Многочисленные исследования, проведенные с применением вегетативных проб, демонстрируют снижение вегетативной реактивности и недостаточное обеспечение физической и умственной деятельности у пациентов с ГБН [9, 12]. Вегетативная дисфункция у данной категории пациентов проявляется преимущественно паттернами симпатикотонии. Все вышеперечисленное свидетельствует о неполноценности функций церебральных регуляторных механизмов, ответственных за адаптацию организма к изменениям внешней и внутренней среды и во многом объясняют проявления дезадаптации у больных с ГБН. В связи с этим вопрос о роли сосудистых факторов, ассоциированных с вегетативной дисфункцией, является актуальным для понимания механизмов развития ГБН. Не существует абсолютных диагностических признаков данного расстройства, а также его лабораторных и рентгенологических маркеров. Применение метода транскраниальной допплерографии (ТКД) у пациентов с ГБН является перспективным в изучении механизмов заболевания.
Цель исследования: оценить состояние мозговой гемодинамики и цереброваскулярной реактивности у пациентов с головной болью напряжения.
Материалы и методы
Было исследовано 105 пациентов молодого возраста (18–35 лет) с головной болью напряжения, в т.ч. с эпизодической ГБН — 51 пациент, хронической ГБН — 54 пациента. Диагноз ставился в соответствии с критериями диагноза Международной классификации ГБ 2-го пересмотра [5]. Оценка характеристик головной боли проводилась по анкете, позволяющей выявить имеющийся у пациента вид ГБ, оценить ее основные качественные и количественные характеристики, провоцирующие факторы, сопровождающие симптомы, способы купирования боли, наличие абузусного фактора. Определение болезненности перикраниальных мышц осуществлялось методом пальпации с последующей оценкой по системе Total Tenderness Score «Общая шкала напряжения» (Langemark M. and Olesen J., 1987).
Исследование церебральных артерий проводилось в триплексном режиме на ультразвуковом сканере Ultima-PA (РАДМИР, Украина), а также на транскраниальном допплеровском анализаторе «Ангиодин» (БИОСС, Россия). Исследовались показатели линейной скорости кровотока (ЛСК) во внутренних сонных (ВСА), передних (ПМА), средних (СМА), задних (ЗМА) мозговых, позвоночных (ПА) и основной (ОА) артериях. Состояние цереброваскулярной реактивности оценивалось с помощью следующих функциональных нагрузок:
— гиперкапническая нагрузка, коэффициент реактивности КрСО2 (Гайдар Б.В.);
— гипервентиляционная нагрузка, коэффициент реактивности КрО2 (Гайдар Б.В.);
— ортостатическая нагрузка, коэффициент реактивности КрОН (Калашников В.И.);
— антиортостатическая нагрузка, коэффициент реактивности КрАОН (Калашников В.И.);
— функциональный нитроглицериновый тест, коэффициент реактивности КрФНТ (Калашников В.И.);
— функциональный метаболический тест, коэффициент реактивности КрФМТ.
Помимо широко используемых коэффициентов реактивности впервые применялся разработанный нами коэффициент реактивности на функциональный метаболический тест (КрФМТ). Тест двусторонней кистевой нагрузки выполнялся по методике M. Stoll (1998) в нашей модификации, рассчитывался КрФМТ в виде отношения ЛСК после проведения теста к фоновой ЛСК.
Контрольная группа (КГ) — 50 клинически здоровых добровольцев обоих полов соответствующего возраста. Статистический анализ и обработка материала проводились с использованием программного пакета Statistiса 6.0. Различия признавались статистически значимыми при значении p < 0,05.
Результаты и обсуждение
Характеристики головной боли у пациентов с ГБН представлены в табл. 1. Головная боль в обеих клинических группах, как правило, определялась как давящая или сжимающая (1-я группа — 84,3 %, 2-я группа — 89,6 %). У подавляющего большинства пациентов боль носила двусторонний характер, с ведущим болевым очагом в теменной (39,7 %), лобной (34,3 %) или затылочной (22,8 %) областях. Реже отмечались лобно-височная, лобно-теменная, теменно-височная и теменно-затылочная локализация. Провоцирующими факторами развития эпизодов ГБН являлись эмоциональные стрессы (37,7 %), получение негативной информации (32,3 %), ношение плотного головного убора (21,5 %), расчесывание (11,6 %). Сопровождающие синдромы проявлялись в виде тошноты (14,2 %), фонофобии (7,6 %), рвоты (5,3 %), фотофобии (3,6 %). Головная боль в обеих группах купировалась приемом анальгетиков (1-я группа — 34,6 %, 2-я группа — 87,4 %). В неврологическом статусе у пациентов с ГБН преобладали признаки вегетативной дисфункции (78,7 %), эмоциональная лабильность (68,3 %), сухожильная гиперрефлексия c расширением рефлексогенных зон (52,6 %) при отсутствии очаговой неврологической симптоматики.
/75.jpg)
В целом у пациентов с ГБН не наблюдалось существенных отличий показателей ЛСК от данных контрольной группы (рис. 1). Гемодинамические нарушения у небольшой части обследованных проявлялись в виде усиления ЛСК и асимметрии ЛСК по магистральным интракраниальным артериям, при этом степень увеличения ЛСК в ряде случаев свидетельствовала о вазоспастических реакциях в отдельных сосудистых бассейнах. Данные реакции отмечалсиь в СМА (у 11,2 % пациентов с ЭГБН и 14,7 % пациентов с ХГБН). Асимметрия ЛСК (20–30 %) по магистральным интракраниальным сосудам выявлялась в ПА (ЭГБН — 17,8 %, ХГБН — 19,6 %), ЗМА (14,9 и 14,5 % соответственно), СМА (13,6 и 14,4 %), ПМА (8,2 и 7,7 %). В контексте данного исследования выявление асимметрии кровотока по СМА (20–25 %) косвенно свидетельствовало о наличии церебральной ангиодистонии, асимметрия ЛСК по ПА (25–30 %) указывала на вероятность наличия начальных признаков дисгемии в вертебробазилярном бассейне.
Исследование ЦВР у пациентов с ГБН выявило определенные закономерности, характерные для различных вариантов данной патологии.
У испытуемых контрольной группы показатели ЦВР составили: КрФМТ — 1,18 ± 0,02, КрФНГ — 0,16 ± 0,04; КрСО2 — 1,33 ± 0,04; КрО2 — 0,46 ± 0,05; КрОН — 0,13 ± 0,03; КрАОН 1,15 ± 0,04. Показатели КрФМТ были достоверно повышены в обеих клинических группах (рис. 2). У пациентов с ЭГБН значения индекса составили 1,24 ± 0,03 (p < 0,05), у пациентов с ХГБН — 1,26 ± 0,03 (p < 0,05). Также у пациентов с ГБН выявлялась гиперреактивность на гиперкапническую нагрузку (КрСО2 — 1,43 ± 0,05 (p < 0,05) в группе с ЭГБН и 1,39 ± 0,07 в группе с ХБН), а также гипореактивность на гипервентиляционную нагрузку, более выраженная при ХГБН (0,38 ± 0,04 и 0,35 ± 0,05 (p < 0,05) соответственно) (рис. 3).
/76_2.jpg)
Данные изменения, по-видимому, связаны с напряжением вазодилататорных механизмов, а также с истощением резерва вазоконстрикции, наиболее проявляющемся в процессе хронизации головной боли. Также отмечалась гиперреактивность на ОН, практически идентичная в обеих клинических группах (0,18 ± 0,04 и 0,19 ± 0,03 соответственно) (рис. 4). При исследовании реактивности на нитроглицериновую пробу и АОН существенных отличий от показателей КГ у пациентов с ГБН не отмечалось.
Результаты проведенных исследований позволяют предположить, что ведущую роль в патогенезе ауторегуляторных нарушений при ГБН играет гуморально-метаболический контур. Как видно из представленных данных, проведение ФМТ, моделирующее ответ церебральных механизмов реактивности на механическое напряжение, стало наиболее информативным методом детекции ауторегуляторных нарушений в обеих клинических группах. Оценка регуляторного ответа на дыхательные нагрузки позволяет выделить ведущие паттерны реактивности при различных вариантах ГБН — напряжение вазодилататорного механизма при ЭГБН и истощение вазоконстрикторного механизма при ХГБН. Участие нейрогенного регуляторного механизма, определяемое гиперреактивностью на ОН, доказывает полифакторный характер изменений при ГБН, связанных с дезадаптацией и дисфункциональными изменениями вегетативных структур.
Cледующей задачей исследования стало изучение влияния на состояние регуляторных механизмов препаратов, традиционно применяемых у пациентов с ГБН, в частности гамалате В6. Выбор данного препарата для исследования связан с особенностями его состава и фармакодинамических механизмов. Гамалате В6 является комбинированным препаратом, влияющим на различные механизмы тормозной модуляции. В состав препарата входят ГАМК, гамма-амино-бета-оксимасляная кислота (ГАБОМ), магния глутамата гидробромид (МГГ) и пиридоксина гидрохлорид [16]. Препараты ГАМК давно и с успехом используются в лечении ГБН. ГАБОМ по сравнению с ГАМК имеет более выраженный тормозной эффект и обладает умеренным противосудорожным действием. МГГ содержит глутаминовую кислоту, являющуюся предшественником ГАМК в ГАМКергических нейронах, и обладает противосудорожным, вегетостабилизирующим и антидепрессивным эффектами. Пиридоксин (витамин В6) участвует в синтезе серотонина и ацетилхолина, благодаря чему способен влиять на тревожную и депрессивную симптоматику. В целом препарат обладает положительным эффектом при ГБН как у взрослых, так и у детей [16].
/77.jpg)
Нами проведено клинико-допплерографическое изучение влияния гамалате В6 на интенсивность головной боли, показатели церебральной гемодинамики и цереброваскулярной реактивности.
Оценка эффективности лечения основывалась на изучении следующих клинико-допплерографических показателей: частота и интенсивность головной боли, ЛСК в СМА и ПА, КрФМТ и КрСО2 у пациентов в динамике (до лечения и по его завершении). Гамалате В6 назначался пациентам в рекомендованной дозе по 1 таблетке 3 раза в сутки вместе с приемом пищи в течение 30 дней.
У пациентов обеих клинических групп отмечалось снижение ЧГБ (с 5,7 ± 4,3 дня/мес до 3,6 ± 2,1 дня/мес в группе с ЭГБН, с 22,8 ± 7,7 дня/мес до 18,5 ± 5,2 дня/мес в группе с ХГБН). Также снижались показатели ИГБ по ВАШ (с 3,5 ± 1,4 б до 1,9 ± 1,1 б в группе с ЭГБН, с 7,3 ± 2,1 б до 5,4 ± 1,9 б в группе с ХГБН) (рис. 5).
Как видно из представленных результатов, высокая эффективность при применении гамалате В6 отмечается у пациентов с ЭГБН.
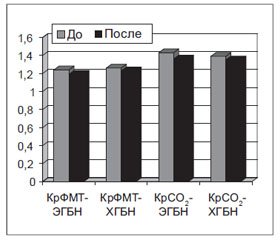
Эффект воздействия гамалате В6 на динамику показателей кровотока в магистральных церебральных артериях заключался не столько в непосредственном влиянии на церебральный кровоток, сколько в регуляции гемодинамических показателей. Это логично вытекает из фармакодинамических характеристик препарата, который не является прямым вазотропным средством, но за счет ГАМКергических свойств, а также влияния на синтез ацетилхолина и серотонина способен оказывать опосредованное сосудорегулирующее действие. На фоне приема гамалате В6 выявлялась тенденция к нормализации изначально несколько повышенных показателей скорости потока в СМА (с 67,7 ± 9,6 см/с до 63,4 ± 7,8 см/с при ЭГБН, с 68,8 ± 7,1 см/с до 62,1 ± 7,6 см/с при ХГБН) (рис. 6). В то же время изначально близкие к нормативным показатели скорости потока по ПА существенно не изменялись.
Также проведенные исследования показали влияние гамалате В6 на показатели сосудистой реактивности (рис. 7). В большей степени это относилось к изначально повышенным КрФМТ и КрСО2 у пациентов с ЭГБН. КрФМТ снизился с 1,24 ± 0,03 до 1,19 ± 0,02 и практически достиг нормативных значений, КрСО2 снизился с 1,43 ± 0,05 до 1, 38, ± 0,06, проявив тенденцию к нормализации. Аналогичная тенденция к нормализации коэффициентов реактивности прослеживалась и в группе с ХГБН, но степень снижения была меньше, чем в группе с ЭБН (КРФМТ снизился с 1,26 ± 0,03 до 1,22 ± 0,04, КрСО2 — с 1,39 ± 0,07 до 1,37 ± 0,05).
Очевидно, что сдвиги сосудистой реактивности с большим трудом поддаются коррекции в процессе хронизации головной боли.
Результаты проведенных исследований показывают положительное влияние гамалате В6 не только на частоту и интенсивность ГБН, но и на допплерографические показатели церебральной гемодинамики. Представляет интерес дальнейшее более углубленное исследование воздействия препарата на различные контуры и механизмы сосудистой ауторегуляции у пациентов с ГБН.
Выводы
1. Церебральная гемодинамика у пациентов с ГБН характеризуется ангиодистоническими явлениями в виде усиления скоростных показателей и функциональных асимметрий кровотока в средних мозговых и позвоночных артериях.
2. Гиперреактивность на функциональный метаболический тест характерна для пациентов как с эпизодическими, так и с хроническими ГБН и отражает напряжение метаболического контура регуляции мозгового кровотока.
3. У большинства пациентов с ЭГБН выявляется гиперреактивность на гиперкапническую нагрузку, вероятно, связанная с напряжением гуморально-метаболического звена регуляции.
4. В группе пациентов с ХГБН преобладает гипореактивность на гипервентиляционную нагрузку, отражающая истощение резерва вазоконстрикции.
5. Применение гамалате В6 в терапии ГБН приводит к снижению показателей частоты и интенсивности боли, более выраженному у пациентов с ЭГБН. Регулирующее влияние гамалате В6 на церебральную гемодинамику заключается в снижении изначально повышенных скоростных показателей потока в СМА, а также в нормализации измененных показателей реактивности. Перспективными являются дальнейшие исследования воздействия гамалате В6 на различные механизмы церебральной ауторегуляции.
/76_2.jpg)

/75.jpg)
/76.jpg)
/77.jpg)
/78.jpg)