Статтю опубліковано на с. 134-139
На сьогодні питання здатності новонароджених і дітей раннього віку відчувати біль не дискутується. Дослідження, проведені в галузі поведінки та фізіології новонароджених, показують, що відразу після народження дитина реагує на больові стимули (Anand and Hickey, 1987; Grunau and Craig, 1987; Levine and Gordon, 1982). Вже з 16-го тижня гестації можлива передача больових імпульсів від периферичних рецепторів до кори головного мозку, а у 26–30 тижнів гестаційного віку плода система ноцицепції сформована повністю. Отже, навіть глибоко недоношені новонароджені виявляють поведінкові та фізіологічні реакції, а також гормональну відповідь на стрес при больовому подразненні [1]. Недоношені, в яких були проведені операції з мінімальною анестезією, мали набагато більший рівень стресу, ускладнень і смертності порівняно з тими, хто отримав ефективний анестезіологічний захист [2]. У той же час неадекватна оцінка болю в дітей може бути основним чинником неадекватного знеболювання, модулювати довготривалі негативні ефекти, пов’язані з досвідом перенесеного болю, і формувати такі патологічні ефекти, як алодинія, гіпералгезія, а також психосоматичні порушення.
Аналіз літературних даних, присвячених больовому синдрому в дітей, свідчить про невирішеність цього питання, зокрема, вказується на часті випадки недооцінки інтенсивності болю і, як наслідок, незадовільну терапію болю. За приклад можна навести опубліковані у 2012 р. результати мультицентрового дослідження, що були проведені у 32 стаціонарних відділеннях (хірургічних і інтенсивної терапії) на базі 8 канадських дитячих госпіталів, в яких було охоплені 3822 дитини віком від 0 до 18 років. Для всіх пацієнтів потрібно було оцінити та задокументувати больовий синдром протягом 24 годин із використанням валідних шкал. Було виявлено, що у третини пацієнтів із тих чи інших причин було неадекватно задокументовано біль. Серед пацієнтів, які мали документальну оцінку болю, у 25 % дітей (n = 263) зареєстровані показники легкого (mild) діапазону болю (1–3/10), у 22 % (n = 238) — помірний (moderate) біль (4–6/10) і в 11 % (n = 116) виявлено тяжкий (severe) біль (7–10/10). У 42 % (n = 455) не було виявлено больового синдрому (0/10) протягом 24-годинного періоду. Великий відсоток середнього і високого ступеня больового синдрому, а також недостатня документація свідчили про незадовільне вирішення цього питання [3]. В іншому мультицентровому дослідженні, в якому вивчалось післяопераційне знеболювання у новонароджених, виявлено, що 12 % дітей після малих оперативних втручань і 7 % дітей після великих травматичних операцій не отримували належного знеболювання в післяопераційному періоді. Основними методами знеболювання у новонароджених була опіоїдна аналгезія (60–84 %), досить часто відзначались випадки заміни анальгетичної терапії седацією [4].
Одними з головних причин неефективної оцінки больового синдрому є відсутність узагальнених підходів щодо оцінки болю в дітей, значна відмінність поведінкових і фізіологічних реакцій дітей різних вікових груп на біль, недостатні зусилля, що стосуються технічної підготовки персоналу й організації менеджменту больового синдрому у дитячих лікарнях.
Сьогодні біль вважається п’ятою життєвою ознакою. Президент Американського товариства болю James Campbell зазначив: «Якщо біль оцінювати як інші життєво важливі ознаки, буде більша ймовірність, що він буде правильно лікуватись. Ми повинні навчати лікарів і медсестер трактувати біль як життєву ознаку. Якість допомоги полягає в тому, що біль потрібно вимірювати та лікувати» [5].
Слід зауважити, що у даний час розроблено десятки шкал для оцінки інтенсивності болю в дітей різних вікових груп, а також у пацієнтів різного профілю (опікові, онкологічні, післяопераційні тощо). Для практикуючого лікаря важливим є вироблення системного й одночасно простого алгоритму оцінки інтенсивності болю, що дасть можливість ефективно лікувати больовий синдром у дітей. Оскільки в наш час не має єдиного золотого стандарту оцінки болю в дітей, то більшість авторів рекомендують поєднувати 2–3 інструменти оцінки болю. Також мають значення використання саме валідних шкал і точна документація інтенсивності больового синдрому у цифрових еквівалентах, що створює умови для ефективної терапії болю. Важливо, щоб у відділеннях був узгоджений погляд на оцінку больового синдрому та використовувалась обмежена кількість шкал.
Нами було проаналізовано ряд європейських та американських керівництв щодо ведення больового синдрому в дітей з метою відбору найбільш ефективних інструментів оцінки болю в дітей, а також спроби систематизувати підходи в оцінці болю в дітей [2, 4–7].
Згідно з рекомендаціями керівництва щодо визначення й оцінки гострого болю в дітей Британського королівського коледжу для медсестер і Британської асоціації болю (Royal College of Nursing & British Pain Society Update of full guideline «The recognition and assessment of acute pain in children 2009»), для вибору відповідних інструментів слід оцінити такі чинники [6]:
1. Вік дитини (недоношена, новонароджена, здатна чи ні до вербального контакту тощо).
2. Біль у клінічному контексті (гострий процедурний біль, післяопераційний біль, післяопераційний біль у присутності батьків удома, больові процедури в інтенсивній терапії).
3. Наявність когнітивних порушень у дитини або обставин, що лімітують поведінкову відповідь дитини (інтубовані пацієнти тощо).
4. Визначити, хто і де буде проводити оцінку болю (лікарі, медсестри, батьки), та їх кваліфікацію.
Усі шкали, що використовують для оцінки больового синдрому, поділяють на три групи [2, 6, 8, 9].
1. Шкали для самооцінки болю (self-report scale) використовуються переважно з 5-річного віку і передбачають відсутність когнітивних порушень і співпрацю пацієнта (Faces Pain Scale (FPS); Faces Pain Scale-Revised (FPS-R); Oucher Pain Scale (OPS), Wong — Baker Faces Pain Rating Scale (WBFPRS), Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), Numercal Rating Scale (NRS) тощо).
2. Поведінкові шкали (behaviours scale) використовуються у новонароджених, дітей, які не можуть вербально повідомити про ступінь вираженості болю, а також у пацієнтів із когнітивними порушеннями (Premature Infant Pain Profile (PIPP), Cries, Requiresoxygen, Increasedvitalsigns, Expression, Sleeplessness (CRIES), Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolability (FLACC), Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Pain Scale (CHEOPS), COMFORT тощо).
3. Фізіологічні параметри (частота пульсу, артеріальний тиск, частота дихання, SpO2, CO2, внутрішньочерепний тиск, рівень глікемії, концентрація кортизолу чи β-ендорфіну тощо).
Оскільки біль є суб’єктивним відчуттям, то одним із головних способів оцінки інтенсивності болю є самооцінка. Такі шкали рекомендовано використовувати з 5-річного віку [9]. За допомогою шкал самооцінки можна оцінити і диференціювати відчуття болю в спокої, під час кашлю чи рухової активності. Серед розроблених шкал самооцінки найбільш надійними і валідними вважаються такі:
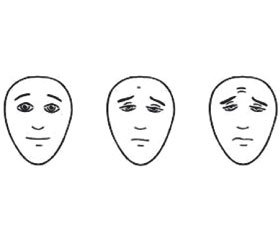
— WBFPRS — шкала оцінки болю за допомогою облич Вонг — Бейкер [9, 10], на якій зображено 6 облич, що супроводжують підписи, які повідомляють про ступінь больового синдрому: стан відсутності болю — максимальна інтенсивність болю. Дитина має вказати, яке обличчя виражає, як сильно в неї болить під час обстеження. Обличчям надаються значення 0–5 або 0–10 (рис. 1).
— FPS-R — шкала інтенсивності больових відчуттів, що оцінюються за обличчями, являє собою 6 зображень. Під час обстеження дитині послідовно, зліва направо, показують обличчя і пропонують вказати на те, яке відповідає відчуттям болю дитини. При цьому не рекомендують вживати характеристики «веселий» чи «сумний», оскільки ця шкала має на меті визначити внутрішні переживання дитини, а не вигляд зображень (рис. 2).
— VAS — візуально-аналогова шкала є простим інструментом, що дозволяє швидко і об’єктивно визначити рівень суб’єктивних больових відчуттів. Використовуючи лінійну шкалу, дитина вказує на інтенсивність больових відчуттів (рис. 3). Існують різні модифікації VAS із можливими градаціями: 0–10 або 0–100. Зазвичай використовується у дітей віком понад 7 років [2, 9].
— NRS — цифрова оцінна шкала, за якою дитина може оцінити свій біль від 0 (зовсім не болить) до 10 (нестерпний біль) (рис. 4). Зазвичай використовується у дітей віком старше 7 років [2, 9].
За результатами оцінних шкал біль класифікують так:
— 0–3 бали — відсутність болю або слабкий біль, що мало турбує;
— 4–6 балів — біль помірний або середнього ступеня інтенсивності;
— 7–10 балів — біль сильної інтенсивності.
У випадку наявності в дитини болю, що оцінюється в 3 бали і вище, слід застосовувати знеболюючі середники. У випадку оцінки болю в 6 балів і вище призначають опіоїди [9, 10].
Щодо вибору найбільш ефективної шкали самооцінки болю, то немає чітких доказів переваг однієї над іншими. В дослідженні D. Tomlinson et al. було проаналізовано 127 статей у таких медичних ресурсах, як Medline, Embase, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, EBSCO Host in the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature Database, в яких було виявлено 14 різних модифікацій оцінних лицевих шкал, з яких було відібрано 4 найбільш валідних: FPS (градація 0–6); FPS-R (0–10); OPS (0–10); WBFPRS (0–10). Зауважено, що всі 4 шкали були однаково ефективними у підтримці психометричних даних і оцінці болю дітьми. Було відзначено, що коли дітям дафвали право вибору лицевої шкали, то вони частіше віддавали перевагу WBFPRS. Для клінічного застосування не було знайдено вагомих підстав, щоб перейти від однієї лицевої шкали до іншої. Для дослідницьких цілей було рекомендовано використовувати FPS-R [10].
Поведінкові шкали створені в результаті спостереження за поведінкою дітей, які відчувають біль. Вони зазвичай складаються з декількох параметрів, які оцінюють. Серед іншого — вираз обличчя, активність, положення рук, ніг, тулуба або поведінка під час сну. Шкали призначені в основному для новонароджених і дітей з обмеженими розумовими можливостями. Використання цих методів має обмеження, пов’язані з тим, що вираження болю відображає фізичний і емоційний спосіб боротьби з болем або момент культурних або сімейних очікувань. Це може призвести до помилкової інтерпретації поведінки. Наприклад, терплячі діти або діти в депресії можуть не виявляти очікуваної реакції на інтенсивність болю [2, 4, 9–11]. У дітей особливо важливою є міміка, оскільки на неї менше впливають попередній досвід болю та інші чинники [2, 6].
Серед валідних поведінкових шкал найчастіше в літературі згадуються такі:
— CRIES — шкала болю, призначена для новонароджених і дітей віком до 6 місяців; оцінює 6 показників: плач, необхідність у кисневій терапії для досягнення сатурації O2 > 95 %, зростання частоти серцевих скорочень і артеріальний тиск порівняно з вихідними даними, вираження болю на обличчі, сон. Оцінка: 0 — немає болю, 10 — максимальна інтенсивність болю (табл. 1).
— PIPP — шкала для недоношених і новонароджених дітей оцінює 7 параметрів: гестаційний вік, поведінку, частоту серцевих скорочень, насичення крові киснем, підняття брів, зажмурення очей, поглиблення носогубної складки. Пацієнт записується на відео впродовж 45 секунд, кожні 3 секунди в час запису фіксуються фізіологічні параметри, а потім відеозапис аналізується. Максимальна кількість балів може сягати 21; 0–6 балів означає, що дитина не відчуває болю, 6–12 — біль помірної інтенсивності, понад 12 балів — біль високої інтенсивності (табл. 1).
— COMFORT — шкала для новонароджених, у тому числі тих, хто перебуває на штучній вентиляції легень (ШВЛ), оцінює такі поведінкові чинники: тривожність, неспокій і ажитація, тонус м’язів, рухи, міміка, реакція на вдих респіратора для дітей, які перебувають на ШВЛ, або плач (для дітей на спонтанному диханні) та 2 фізіологічних параметри: частота серцевих скорочень, середній артеріальний тиск. Дитина спостерігається упродовж 2 хвилин, кожні 20 секунд записуються згадані вище фізіологічні показники. Незадовго до кінця спостереження оцінюється м’язовий тонус (шляхом підняття рук і ніг дитини). Кожний показник оцінюється за шкалою від 1 до 5 балів. Можливий діапазон балів — 9–45. Оцінка в межах 17–26 свідчить про адекватне знеболювання (табл. 1).
— FLACC — ця шкала використовується для оцінки післяопераційного болю у немовлят та дітей молодшого віку до 7 років. У ній аналізуються 5 параметрів: вираз обличчя, рухи ніг, рухова активність, плач і здатність до заспокоєння. Можливий діапазон оцінки інтенсивності болю від 0 (не болить) до 10 (дуже сильний біль) (табл. 1).
— Noncomunicating Children’s Pain Checklist Postoperative Version (NCPC-PV) — шкала використовується для оцінки післяопераційного болю у дітей із когнітивними розладами, а також у немовлят на підставі опитування опікунів і доглядаючого персоналу. З цією ж метою використовуються модифікована шкала Revised FLACC, індивідуалізована числова рейтингова шкала (Individualized Numeric Rating Scale, INRS) та інші.
Щодо фізіологічних показників, рекомендовано використовувати їх у поєднанні з самооцінними або поведінковими шкалами, оскільки існує чимало причин, що можуть спотворити їх інтерпретацію. Зокрема, зростання частоти серцевих скорочень, артеріального тиску, частоти дихання може бути відповіддю на розлучення з батьками, страх, а також результатом основного захворювання (сепсис, дихальна недостатність, гіповолемія, гіпертермія, застосування катехоламінів тощо).
Необхідно звернути увагу на те, що значну частину пацієнтів педіатричних відділень інтенсивної терапії становлять діти з когнітивними порушеннями та неврологічним дефіцитом. Оцінювання ступеня болю у таких пацієнтів має свої особливості, без урахування яких неможливо ефективно проводити оцінку і терапію больового синдрому. Для даної групи пацієнтів розроблені спеціалізовані шкали (NCPC-PV, Revised FLACC, INRS та ін.).
На завершення зазначимо, що, незважаючи на розробку численних керівництв з ведення болю у дітей, більшість авторів вказують на потребу в подальших дослідженнях у цьому питанні. Автор статті не мав на меті перерахувати всі існуючі інструменти оцінки болю у дітей. Метою літературного огляду було показати, що в арсеналі лікарів, які працюють з дітьми, є достатньо валідних засобів оцінки больового сидрому. На наш погляд, основна проблема щодо вирішення цього питання лежить в організаційній площині, а саме в імплементації існуючих шкал у клінічну практику та підготовку персоналу.
Висновки
1. Проблема оцінки болю в педіатричних пацієнтів є актуальною, про що свідчать численні літературні дані.
2. Вже від народження діти здатні відчувати біль, що вимагає від лікарів постійної настороженості у цьому питанні.
3. Для успішного вибору засобів оцінки болю у дітей потрібно враховувати вік дитини, наявність когнітивних порушень, клінічну інтерпретацію болю (процедурний, післяопераційний тощо), умови виникнення болю (інтенсивна терапія, потреба у ШВЛ, хірургічне відділення, спостереження батьків).
4. У новонароджених і пацієнтів віком до 5 років рекомендовано використовувати комплексні шкали, що включають поведінкові характеристики та фізіологічні параметри.
5. Для дітей віком старше 5 років пріоритетними є самооцінні шкали.
6. Оцінку гострого болю слід проводити кожні 4–6 годин з обов’язковою документацією (бальною оцінкою), що дасть змогу ефективно лікувати біль.
7. Слід застосовувати валідні шкали та узгоджений погляд усього колективу відділення на їх використання.
Конфлікт інтересів. Автор заявляє про відсутність конфлікту інтересів при підготовці даної статті.

/134-139/135-1.jpg)
/134-139/136-1.jpg)
/134-139/136-2.jpg)
/134-139/137-1.jpg)