Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» №6(101), 2019
Вернуться к номеру
Comparison of combined general anesthesia with and without epidural morphine on the background of redox therapy in cancer patients with multiorgan resections
Авторы: M.V. Krasnoselskiy(1), Ye.M. Krutko(1), E.S. Protcenko(2), Ye.V. Shulga(2), M.V. Shulga(1)
(1) — State Institution "Grigoriev Institute for Medical Radiology of National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine", Kharkiv, Ukraine
(2) — V.N. Karazin Kharkiv National University, Kharkiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
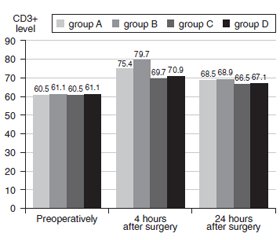
Актуальність. На сьогодні недостатньо даних щодо післяопераційного епідурального знеболювання з використанням морфіну та проведення окисно-відновної терапії в онкохворих із мультиорганними оперативними втручаннями з подальшою оцінкою показників імунітету. Мета роботи: вивчення інтраопераційного використання епідурального морфіну порівнянo з комбінованою загальною епідуральною анестезією, а також проведення окисно-відновної терапії в онкохворих із мультиорганними оперативними втручаннями з оцінкою показників імунітету для забезпечення анестезії з випереджаючою терапією можливих ускладнень та отримання більш комфортного стану пацієнтів. Матеріали та методи. Під час дослідження було обстежено 117 пацієнтів із місцево-поширеним пухлинним процесом шлунково-кишкового тракту з мультиорганними хірургічними втручаннями за життєвими показаннями (67,6 ± 3,7 року). Усі пацієнти були розподілені на чотири групи залежно від типу анестезії та антиоксидантної терапії. Були виділені групи з інтраопераційним використанням епідурального морфіну та без нього. Як антиоксидантну терапію використовували L-орнітин L-аспартат з комплексом кверцетину з повідоном. Вимірювали показники клітинного та гуморального імунітету на прикладі субпопуляційного визначення відносної кількості лімфоцитів CD3+ та IgA до і через 4 і 24 години після операції. Загальну якість життя, пов’язану зі здоров’ям, оцінювали із застосуванням стандартного «Короткого опитувальника оцінки статусу здоров’я» SF-36 за науково обґрунтованою методологією. Результати. Отримані результати свідчать за те, що в групі з використанням епідурального морфіну ступінь ефективності знеболювання був достатнім, але були зареєстровані ускладнення, у тому числі у вигляді апное при використанні морфіну та незначного погіршення показників імунітету. При застосуванні окисно-відновної терапії ми досягли як поліпшення якості життя, так і більш значного покращання показників імунітету. Висновки. Таким чином, проведення комбінованої епідуральної анестезії без використання морфіну на тлі корекції окисно-відновного метаболізму в онкохворих із мультиорганними оперативними втручаннями більш комфортне для пацієнтів, менш небезпечне через відсутність розвитку апное, психоемоційно і економічно виправдане, що свідчить про її пріоритетне використання.
Актуальность. На сегодня недостаточно данных о послеоперационном эпидуральном обезболивании с использованием морфина и проведении окислительно-восстановительной терапии у онкобольных с мультиорганными оперативными вмешательствами с оценкой показателей иммунитета. Цель работы: изучение интраоперационного использования эпидурального морфина по сравнению с комбинированной общей эпидуральной анестезией, а также проведение окислительно-восстановительной терапии у онкобольных с мультиорганными оперативными вмешательствами с оценкой показателей иммунитета для обеспечения анестезии с опережающей терапией возможных осложнений и получения более комфортного состояния пациентов. Материалы и методы. В ходе работы было обследовано 117 пациентов с местно-распространенным опухолевым процессом желудочно-кишечного тракта с мультиорганными хирургическими вмешательствами по жизненным показаниям (67,6 ± 3,7 года). Все пациенты были разделены на четыре группы в зависимости от типа анестезии и антиоксидантной терапии. Были выделены группы с интраоперационным использованием эпидурального морфина и без него. В качестве антиоксидантной терапии использовали L-орнитин L-аспартат с комплексом кверцетина с повидоном. Измерялись показатели клеточного и гуморального иммунитета на примере субпопуляционного определения относительного количества лимфоцитов CD3+ и IgA до операции и через 4 и 24 часа после операции. Общее качество жизни, связанное со здоровьем, оценивали с применением стандартного «Краткого опросника оценки статуса здоровья» SF-36 по научно обоснованной методологии. Результаты. Полученные результаты свидетельствуют о том, что в группе с использованием эпидурального морфина степень эффективности обезболивания была достаточной, но были зарегистрированы осложнения, в том числе в виде апноэ при использовании морфина и незначительное ухудшение показателей иммунитета. При применении окислительно-восстановительной терапии мы достигли как улучшения качества жизни, так и более значительного улучшения показателей иммунитета. Выводы. Таким образом, проведение комбинированной эпидуральной анестезии без использования морфина на фоне коррекции окислительно-восстановительного метаболизма у онкобольных с мультиорганными оперативными вмешательствами более комфортно для пациентов, менее опасно из-за отсутствия развития апноэ, психоэмоционально и экономически оправдано, что свидетельствует о ее приоритетном использовании.
Background. There are insufficient data on postoperative epidural anesthesia using morphine and conducting redox therapy in cancer patients with multiorgan resections with the assessment of immunological parameters. This work studies the intraoperative use of epidural morphine as compared with combined general epidural anesthesia, as well as the redox therapy in cancer patients with multiorgan resections with an evaluation of the indicators of immunity to provide anesthesia with advanced therapy of possible complications and obtain a more comfortable condition of patients. Materials and methods. The study examined 117 cancer patients with locally advanced tumor process of the gastrointestinal tract with multiorgan surgical interventions for health reasons (67.6 ± 3.7 years old). All patients were divided into four groups according to the type of anesthesia and type of antioxidant therapy. The groups with intraoperative epidural morphine use and without it were distinguished. L-ornithine L-aspartate with quercetin complex with povidone was used as an antioxidant therapy. The overall health-related quality of life was evaluated using the standard Short Health Status Assessment Questionnaire SF-36, using the evidence-based methodology. Results. The results suggest that in the group using epidural morphine, the degree of anesthesia effectiveness was sufficient, but there were registered the complications, including in the form of apnea while using morphine and a slight deterioration in immunity parameters. When applying the redox therapy, we have achieved improvement both in quality of life and more significantly in immunity. Conclusions. Thus, combined epidural anesthesia without morphine against the background of correction of redox metabolism in cancer patients with multiorgan resections is more comfortable for patients, less dangerous due to the lack of development of apnea, psychoemotional and economically justified, which indicates its priority using.
епідуральний морфін; окисно-відновна терапія; мультиорганні оперативні втручання; комбінована загальна епідуральна анестезія
эпидуральный морфин; окислительно-восстановительная терапия; мультиорганные оперативные вмешательства; комбинированная общая эпидуральная анестезия
epidural morphine; redox therapy; multiorgan resections; combined general epidural anesthesia
Introduction
Materials and methods
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
1. Fitzmaurice C., Allen C., Barber R.M., Barregard L., Bhutta Z.A. et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2017. Vol. 3(4). P. 524-548. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688.
2. Bartos A., Bartos D., Stoian R., Szabo B., Cioltean C. et al. Short-term outcome and survival after multiorgan resection for locally advanced colo-rectal cancer. Identification of risk factors. Clinical and Translational Oncology. 2017. Vol. 19. P. 750-760. PMID: 30588919.
3. Abdel-Ghaffar H.S., Mohamed S.A., Fares K.M. Combined intrathecal morphine and dexmedetomidine for postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing major abdominal cancer surgery. Pain Med. 2016. Vol. 17(11). P. 2109-2118. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnw031.
4. Jiang Y., Li J., Lin H., Huang Q., Wang T. et al. The efficacy of gabapentin in reducing pain intensity and morphine consumption after breast cancer surgery: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. Vol. 97(38). P. 11581. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011581.
5. Zotou A., Siampalioti A., Tagari P., Paridis L., Kalfarentzos F. et al. Does epidural morphine loading in addition to thoracic epidural analgesia benefit the postoperative management of morbidly obese patients undergoing open bariatric surgery? A pilot study. Obes. Surg. 2014. Vol. 24(12). P. 2099-2108. doi: 10.1007/s11695-014-1305-z.
6. Hou M., Zhou N.B., Li H., Wang B.S., Wang X.Q. et al. Morphine and ketamine inhibit immune function of gastric cancer patients by increasing percentage of CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells in vitro. J. Surg. Res. 2016. Vol. 203(2). P. 306-312. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.02.031.
7. Ferro A., Peleteiro B., Malvezzi M., Bosetti C., Bertuccio P. et al. Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980–2011), with predictions to 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur. J. Cancer. 2014. Vol. 50(7). P. 1330-1344. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.01.029. Epub 2014 Mar 17.
8. Pei L., Tan G., Wang L., Gun W., Xiao B. et al. Comparison of Combined General-Epidural Anesthesia with General Anesthesia Effects on Survival and Cancer Recurrence: A Meta-Analysis of Retrospective and Prospective Studies. Plos One. 2014. Vol. 9(12). P. 1146-1167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114667.
9. Gao H., Meng X.-Y., Wang H.-Q., Zhu F.-F., Guo A.-L. Association between anaesthetic technique and oncological outcomes after colorectal carcinoma liver metastasis resection. International Journal of Medical Sciences. 2019. Vol. 16(2). P. 337-342. doi: 10.7150/ijms.28016.
10. Li Y., Dong H., Tan S., Qian Y., Jin W. Effects of thoracic epidural anesthesia/analgesia on the stress response, pain relief, hospital stay, and treatment costs of patients with esophageal carcinoma undergoing thoracic surgery: A single-center, randomized controlled trial. Medicine. 2019. Vol. 98(7). P. 143-162. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000014362.
11. Ozcan S., Ozer A.B., Yasar M.A., Erhan O.L. Effects of combined general anesthesia and thoracic epidural analgesia on cytokine response in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2016. Vol. 19(4). P. 436-442. doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.183308.
12. Zabolotskikh I., Trembach N. Safety and efficacy of combined epidural/general anesthesia during major abdominal surgery in patients with increased intracranial pressure: a cohort study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015. Vol. 15(1). P. 71-76. doi: 10.1186/s12871-015-0056-2.
13. Yang H.Y., Lee T.H. Antioxidant enzymes as redox-based biomarkers: a brief review. BMB Rep. 2015. Vol. 48(4). P. 200-208. PMID: 25560698.
14. Schmitt B., Vicenzi M., Garrel C., Denis F.M. Effects of N-acetylcysteine, oral glutathione (GSH) and a novel sublingual form of GSH on oxidative stress markers: a comparative crossover study. Redox Biology. 2015. Vol. 6. P. 198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.07.012.
15. Rinnerthaler M., Bischof J., Streubel M., Trost A., Richter K. Oxidative stress in aging human skin. Biomolecules. 2015. Vol. 5(2). P. 545-589. doi: 10.3390/biom5020545.

/72.jpg)
/72_2.jpg)
/73.jpg)