Газета «Новости медицины и фармации» №3 (715), 2020
Вернуться к номеру
Надання медичної допомоги для лікування коронавірусної хвороби (COVID-19)
Разделы: Официальная информация
Версия для печати
| 02.04.2020 | № 762 |
Вступ
І. Паспортна частина
ІІ. Загальна частина
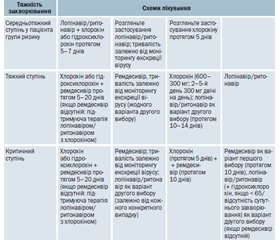
ІІІ. Основна частина
IV. Перелік літературних джерел, використаних при розробці клінічного протоколу медичної допомоги
1. Interim clinical guidance for adults with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 in Belgium. https://epidemio.wiv-isp.be/ID/Documents/Covid19/COVID-19_InterimGuidelines_Treatment_ENG.pdf.
2. Liu Y., Yan L.-M., Wan L., Xiang T.-X., Le A., Liu J.-M. et al. Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2020. 0. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30232-2.
3. Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z. et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Published Online First. 11 March 2020. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3.
4. Agostini M.L., Andres E.L., Sims A.C., Graham R.L., Sheahan T.P., Lu X. et al. Coronavirus Susceptibility to the Antiviral Remdesivir (GS-5734) Is Mediated by the Viral Polymerase and the Proofreading Exoribonuclease. mBio. 2018. 9. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00221-184; Sheahan T.P., Sims A.C., Graham R.L., Menachery V.D., Gralinski L.E., Case J.B. et al. Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017. 9. 3653.
5. Sheahan T.P., Sims A.C., Leist S.R., Schäfer A., Won J., Brown A.J. et al. Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020. 11. 222.
6. Gordon C.J., Tchesnokov E.P., Feng J.Y., Porter D.P., Gotte M. The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Biol. Chem. 2020. jbc.AC120.013056.
7. Wang M., Cao R., Zhang L., Yang X., Liu J., Xu M. et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell. Research. 2020. 1–3.
8. Brown A.J., Won J.J., Graham R.L., Dinnon K.H., Sims A.C., Feng J.Y. et al. Broad spectrum antiviral remdesivir inhibits human endemic and zoonotic deltacoronaviruses with a highly divergent RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Antiviral. Res. 2019. 169. 104541.
9. Vincent M.J., Bergeron E., Benjannet S., Erickson B.R., Rollin P.E., Ksiazek T.G. et al. Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus infection and spread. Virology Journal. 2005. 2. 69.
10. Keyaerts E., Vijgen L., Maes P., Neyts J., Van Ranst M. In vitro inhibition of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus by chloroquine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004. 323. 264-268.
11. De Wilde A.H., Jochmans D., Posthuma C.C., Zevenhoven-Dobbe J.C., van Nieuwkoop S., Bestebroer T.M. et al. Screening of an FDA-Approved Compound Library Identifies Four Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication in Cell Culture. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014. 58. 4875-4884.
12. Barnard D.L., Day C.W., Bailey K., Heiner M., Montgomery R., Lauridsen L. et al. Evaluation of immunomodulators, interferons and known in vitro SARS-coV inhibitors for inhibition of SARS-coV replication in BALB/c mice. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2006. 17. 275-284.
13. Multicenter collaboration group of Department of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province and Health Commission of Guangdong Province for chloroquine in the treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia. [Expert consensus on chloroquine phosphate for the treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia]. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2020. 43. E019.
14. Biot C., Daher W., Chavain N., Fandeur T., Khalife J., Dive D. et al. Design and Synthesis of Hydroxyferroquine Derivatives with Antimalarial and Antiviral Activities. J. Med. Chem. 2006. 49. 2845-2849.
15. Yao X., Ye F., Zhang M., Cui C., Huang B., Niu P. et al. In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin. Infect. Dis. Published. Online First. 9 March 2020. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa237.
16. Gautret P., Lagier J.-C., Parola P., Hoang V.T., Meddeb L., Mailhe M. et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 2020. 105949.
17. Chen F., Chan K.H., Jiang Y., Kao R.Y.T., Lu H.T., Fan K.W. et al. In vitro susceptibility of 10 clinical isolates of SARS coronavirus to selected antiviral compounds. J. Clin. Virol. 2004. 31. 69-75.
18. Yamamoto N., Yang R., Yoshinaka Y., Amari S., Nakano T., Cinatl J. et al. HIV protease inhibitor nelfinavir inhibits replication of SARS-associated coronavirus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004. 318. 719-725.
19. Chu C.M., Cheng V.C.C., Hung I.F.N., Wong M.M.L., Chan K.H., Chan K.S. et al. Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings. Thorax. 2004. 59. 252-256.
20. Chan J.F.W., Chan K.-H., Kao R.Y.T., To K.K.W., Zheng B.-J., Li C.P.Y. et al. Broad-spectrum antivirals for the emerging Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Journal of Infection. 2013. 67. 606-616.
21. Chan J.F.-W., Yao Y., Yeung M.-L., Deng W., Bao L., Jia L. et al. Treatment With Lopinavir/Ritonavir or Interferon-β1b Improves Outcome of MERS-CoV Infection in a Nonhuman Primate Model of Common Marmoset. J. Infect. Dis. 2015. 212. 1904-1913.
22. The Efficacy of Lopinavir Plus Ritonavir and Arbidol Against Novel Coronavirus Infection — Full Text View — ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04252885 (accessed 24 Mar 2020).
23. Cao B., Wang Y., Wen D., Liu W., Wang J., Fan G. et al. A Trial of Lopinavir — Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. NEJMoa2001282.
24. Dobson J., Whitley R.J., Pocock S., Monto A.S. Oseltamivir treatment for influenza in adults: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. The Lancet. 2015. 385. 1729-1737.
25. Kamal M.A., Gieschke R., Lemenuel-Diot A., Beauchemin C.A.A., Smith P.F., Rayner C.R. A Drug-Disease Model Describing the Effect of Oseltamivir Neuraminidase Inhibition on Influenza Virus Progression. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2015. 59. 5388-5395.
26. Organization WH. Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: interim guidance, 13 March 2020. Published Online First. 2020. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331446 (accessed 16 Mar 2020).
27. Russell C.D., Millar J.E., Baillie J.K. Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury. Lancet. 2020. 395. 473-475.
28. Schwartz D.A. An Analysis of 38 Pregnant Women with COVID-19, Their Newborn Infants, and Maternal-Fetal Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Maternal Coronavirus Infections and Pregnancy Outcomes. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. Published Online First. 17 March 2020. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2020-0901-SA.
29. Chen H., Guo J., Wang C., Luo F., Yu X., Zhang W. et al. Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: a retrospective review of medical records. The Lancet. 2020. 395. 809-815.
30. Qiao J. What are the risks of COVID-19 infection in pregnant women? The Lancet. 2020. 395. 760-762.
31. CDC. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prepare/children.html (accessed 24 Mar 2020).
32. Dong Y., Mo X., Hu Y., Qi X., Jiang F., Jiang Z. et al. Epidemiological Characteristics of 2143 Pediatric Patients With 2019 Coronavirus Disease in China. Pediatrics. 2020. Е20200702.
33. CDC. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) and Breastfeeding. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/breastfeeding-special-circumstances/maternal-or-infant-illnesses/covid-19-and-breastfeeding.html (accessed 24 Mar 2020).
34. Lu X., Zhang L., Du H., Zhang J. SARS-CoV-2 Infectionin Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2005073.
35. Zimmermann P., Nigel C. Coronavirus Infectionsin Children Including COVID-19 An Overview of the Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, Treatmentand Prevention Options in Children. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. March 12, 2020. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002660.

/16_u.jpg)
/16_u2.jpg)
/17_u.jpg)
/17_u2.jpg)
/17_u3.jpg)