Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 17, №7, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Оцінка молекулярної мішені адемолу методом хемоінформатики
Авторы: Семененко С.І. (1), Семененко А.І. (1), Редькін Р.Г. (2), Семененко І.Ф. (1)
(1) — Вінницький національний медичний університет імені М.І. Пирогова, м. Вінниця, Україна
(2) — Харківський національний університет імені В.Н. Каразіна, м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
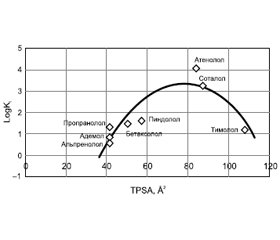
Актуальність. Глутаматна ексайтотоксичність та внутрішньочерепна гіпертензія являють собою потенційні мішені щодо можливих розробок патогенетичної терапії уражень мозку, зокрема тих, що асоційовані з високими значеннями внутрішньочерепного тиску. Мета. Методами хемоінформатики обґрунтувати внутрішньовенне застосування адемолу, виявити здатність адемолу блокувати β-адренорецептори, а також за критеріями лікоподібності та біодоступності оцінити можливість його проходження через гематоенцефалічний бар’єр (ГЕБ). Матеріали та методи. Всі обчислення молекулярних дескрипторів були зроблені за допомогою програмного комплексу SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, розрахункової платформи та Molinspiration Cheminformatics v2016.09, доступних on-line. Результати. Молекулярна маса адемолу не перевищує 500, середній показник ліпофільності розрахований за допомогою програмного комплексу [5], знаходиться для наведених сполук у прийнятному діапазоні. Для адемолу величина LogP дорівнює 2,736, що вище, ніж у ремантадину (2,456), однак нижче, ніж у пропранололу (2,967). Визначено загальну площу полярних поверхонь молекул (TPSA), що розраховується на основі методики, опублікованої Ertl et al. [6] у вигляді внесків суми площин атомів О та N та інших, у складі функціональних груп полярних фрагментів. Для предикації проникнення адемолу через ГЕБ використали розраховані in silico дескриптори — усереднену ліпофільність, що виявилася близькою до описаного раніше коефіцієнту ліпофільності у суміші октанолу та фосфатного буфера [9], та TPSA. Кореляція афінітету (LogKi, nM) з полярністю для відомих β-адреноблокаторів та адемолу описується як параболічна поліноміальна функція другого порядку. Висновки. Побудовано модель кореляції афінітету від ліпофільності для ряду β-адреноблокаторів та передбачено афінність адемолу, що наближається до високоафінних неселективних β-адреноблокаторів.
Background. Glutamate excitotoxicity and intracranial hypertension are potential targets for possible developments of pathogenetic therapy of brain lesions, in particular those associated with high intracranial pressure. The purpose of the work: using chemoinformatic methods to justify the intravenous use of ademol, to detect the ability of ademol to block β-adrenergic receptors, as well as to assess the possibility of its passage through the blood-brain barrier in terms of drug-likeness and bioavailability criteria. Materials and methods. All calculations of molecular descriptors were made using the software package SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, computing platform and Molinspiration Cheminformatics v2016.09, available online. Results. The molecular weight of ademol does not exceed 500, the average lipophilicity value calculated using software package is in the acceptable range for the above compounds. For ademol, the value of LogP is 2,736, which is higher than that of rimantadine (2,456), but lower than that of propranolol (2,967). The total polar surface area is calculated based on the methodology developed by Ertl et al. in the form of contributions of the sum of the planes of O- and N-atoms etc., as a part of the functional groups of polar fragments. To predict ademol pe-netration through the blood-brain barrier, descriptors calculated in silico were used — average lipophilicity, which appeared to be close to previously described lipophilicity coefficient in a mixture of octanol and phosphate buffer, and the total polar surface area of mo-lecules. Affinity correlation (LogKi, nM) with polarity for known β-blockers and ademol is described as a second-degree parabolic polynomial function. Conclusions. A model of affinity correlation with lipophilicity for a number of β-blockers was created and the affinity of ademol is predicted, which is close to that of high-affi-nity non-selective β-blockers.
адемол; хемоінформатика; внутрішньочерепний тиск; черепно-мозкова травма; гематоенцефалічний бар’єр
ademol; chemoinformatics; intracranial pressure; traumatic brain injury; blood-brain barrier
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати та обговорення
/50_2.jpg)
Висновки
- Семененко С.І., Ходаківський О.А., Семененко О.М., Яковлева О.О., Семененко Н.О. Оцінка нейропротекторних властивостей Адемолу в умовах експериментальної черепно-мозкової травми. Вісник Вінницького національного університету ім. М.І. Пирогова. 2019. № 2. Т. 23. С. 109-212.
- Mishra N.K., Kumar M., Raghava G.P. Support vector machine based prediction of glutathione S-transferase proteins. Protein Pept. Lett. 2007. Vol. 14(6). P. 575-580. Cited 13 times.
- Nisoli E., Tonello C., Landi M., Carruba M.O. Functional
- studies of the first selective β3-adrenergic receptor antagonist SR 59230A in rat brown adipocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1996. Vol. 49(1). Р. 7-14.
- Zhuravel' I.A., Kovalenko S.N., Ivashchenko A.V., Balakin K.V., Chernykh V.P., Skorenko A.V., Ivanenkov Ya.A. Zhurnal organichnoi ta farmatsevtichnoi khimii. Journal of organic and pharmaceutical chemistry. 2005. Vol. 3(1). P. 6-11.
- Kaiser J.H., Flammer J., Scumfig D., Hendrickson P. Long term follow up of glaucoma patients treated with beta blockers. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1994. Vol. 38 (Suppl). S 156-S160.
- Ertl P., Rohde B., Selzer P. Fast Calculation of Molecular Polar Surface Area as a Sum of Fragment-Based Contributions and Its Application to the Prediction of Drug Transport Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2000. Vol. 43(20). P. 3714-3717.
- Veber D.F., Johnson S.R., Cheng H.-Y., Smith B.R., Ward K.W., Kopple K.D. Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002. Vol. 45(12). P. 2615-2623.
- Wei Wang, Hitoshi Sasaki, Du-Shieng Chien Z. and Vincent H.L. Lee. Lipophilicity influence on conjunctival drug penetration in the pigmented rabbit: a comparison with corneal penetration. Current Eye Research. 1991. Vol. 10(6). Р. 571-579.
- A simple, robust, and efficient description of n-octanol/water partition coefficient for drug design using the GB/SA approach. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014. Vol. 54(12). Р. 3284-3301.
- A BOILED-Egg to predict gastrointestinal absorption and brain penetration of small molecules. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016. М11(11). Р. 1117-1121.

/49.jpg)
/50.jpg)