Розлади спектра аутизму (РАС) у дітей — глобальна проблема, яка є пріоритетною в сучасній дитячій неврології та психіатрії [36]. Розробка дієвих способів лікування РАС неможлива без поглиблення розуміння етіології і патогенезу хвороби. Сьогодні дослідження спрямовані на вивчення нейротропного впливу інфекційних агентів, системної запальної реакції та автоімунного енцефаліту, асоційованого з генетичним дефіцитом фолатного циклу. Усі ці шляхи церебрального ушкодження потенційно можуть бути об’єктами терапевтичних втручань з метою досягнення нейропротекторного ефекту.
Зараз не викликає сумнівів факт, що основним чинником, асоційованим з РАС у дітей, є генетичний дефіцит фолатного циклу (ГДФЦ). Таке твердження підкріплене результатами 5 метааналізів рандомізованих контрольованих клінічних досліджень [54, 64, 80, 82, 88], а дані ще одного метааналізу вказують на те, що гіпергомоцистеїнемія, специфічний біохімічний феномен саме для ГДФЦ, характерний для дітей з РАС у цілому, тобто є класовою ознакою цієї когорти пацієнтів [41].
Результати клінічних досліджень демонструють, що патогенні поліморфні варіанти генів фолатного циклу (ФЦ) здатні призводити до розвитку клінічних симптомів принаймні трьома шляхами: а) метаболічним, тісно пов’язаним з феноменом гіпергомоцистеїнемії та індукцією оксидативного стресу [27, 34, 41]; б) імунозалежним, пов’язаним з імунною дисфункцією і зумовленим розвитком імуноопосередкованих ускладнень [36, 47]; в) генорегуляторним, опосередкованим аномальною дерепресією інших патогенних мутацій/поліморфізмів у геномі носія внаслідок порушення процесів метилювання ДНК [45].
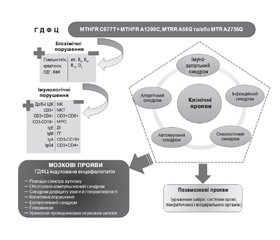
Слід брати до уваги, що ФЦ функціонує у нерозривній єдності з іншими біохімічними циклами, такими як цикл метіоніну, редокс-система, пуриновий обмін, цикл жирних кислот та шлях метаболізму, пов’язаний з 4-тетрагідронеоптерином, тому порушення в суміжних біохімічних процесах можуть призводити до подібних клінічних наслідків, що й ГДФЦ (рис. 1) [35].
/67.jpg)
У даній роботі ми наводимо власний багаторічний досвід спостереження за дітьми дослідної групи (ДГ) з ГДФЦ у кількості 225 осіб віком від 2 до 9 років, у яких відзначалися клінічні появи РАС, порівняно із контрольною групою (КГ), до якої віднесли 51 психічно здорову дитину аналогічної статі та віку [1–8]. Дослідження були проведені у період з 2010 по 2021 р. на базі Науково-дослідного інституту експериментальної і клінічної медицини Національного медичного університету імені О.О. Богомольця та спеціалізованої нейроімунологічної клініки Vivere. Клінічний діагноз РАС був встановлений висококваліфікованими дитячими психіатрами за критеріями DSM-IV-TR, DSM-V та –ICD-10 (атиповий дитячий аутизм, F84.1). Усі дослідження були виконані із дотриманням біоетичних вимог (протокол комісії з біоетики НМУ імені О.О. Богомольця № 140 від 21.12.2020 р.).
Результати власних спостережень та дані сучасної літератури дозволяють стверджувати, що для дітей із ГДФЦ є характерним специфічний патерн біохімічних змін, нетиповий для здорових дітей і асоційований саме з патогенними поліморфними замінами нуклеотидів у генах ензимів циклу фолієвої кислоти. Відзначаються гіпергомоцистеїнемія, дефіцит вітамінів (В6, В9, В12, D3), гіперкреатинінемія, підвищені сироваткові концентрації лактатдегідрогенази та креатинфосфокінази [5, 15, 56, 102, 107]. Механізм розвитку цих порушень може бути складним і багатокомпонентним, однак усі біохімічні відхилення тісно асоційовані саме з патогенними поліморфізмами генів ФЦ, а їх вираженість залежить від виду, кількості і композиції патогенних замін нуклеотидів. Найсприятливішим у біохімічному плані вважається генотип MTHFR C677T, а найтяжчим — генотип із комбінацією всіх чотирьох основних патогенних поліморфізмів MTHFR C677T + MTHFR A1298C + MTR A2756G + MTRR A66G [5].
Так, дефіцит ензимів ФЦ напряму призводить до гіпергомоцистеїнемії [18]. Дисбаланс низки вітамінів викликає порушення всмоктування нутрієнтів у тонкій кишці і розвиток персистуючого імунозапального ентероколіту [37], що віддзеркалюється на харчовій поведінці дитини, відмові або вибірковості їжі [65]. Підвищення сироваткової концентрації креатиніну, лактатдегідрогенази і креатинфосфокінази є наслідком оксидативного стресу [27] через пряму ушкоджуючу дію гомоцистеїну на білки і фосфоліпіди клітин, мітохондріальну дисфункцію [85].
Наведений комплекс біохімічних тестів може бути використаний у діагностичному процесі як для скринінгу ГДФЦ, так і при клінічному моніторингу дітей з РАС, а також вказані біохімічні зсуви можуть бути об’єктом терапевтичних втручань. У метааналізі клінічних досліджень доведено ефективність специфічної метаболічної терапії метилкобаламіном у дозі 64,5–75 мг/кг для корекції біохімічних порушень, індукованих ГДФЦ, і пов’язаного з цим зменшення проявів РАС у дітей [84].
Дані з оцінки імунного статусу дозволяють дійти висновку, що ГДФЦ призводить до розвитку особливої форми первинного імунодефіциту з варіабельним імунологічним фенотипом, із переважним залученням NK-, NKT-клітин, СD8+ цитотоксичних Т-лімфоцитів, мієлопероксидази фагоцитів, що нерідко комбінуються з дисімуноглобулінемією [6, 86, 87, 103, 104]. Цей імунодефіцит має дисметаболічну природу, оскільки основні його компоненти асоційовані зі специфічними біохімічними порушеннями, характерними для ГДФЦ. Указаний імунодефіцит проявляється у вигляді синдрому зниженої імунорезистентності через брак певних протективних імунних чинників [103, 104] та імунну дизрегуляцію [47, 85] внаслідок дисбалансу, зумовленого дефіцитом компонентів імунної системи з реципрокними властивостями (рис. 2) [6].
Розвиток імуносупресії при ГДФЦ можна пояснити як прямим імунотоксичним впливом гомоцистеїну та креатиніну [18], так і дефіцитом есенціальних вітамінів, необхідних для належного функціонування імунної системи [15]. Важливими можуть бути ознаки мітохондріальної дисфункції, що передбачає енергетичне голодування [85], та порушення обміну пуринових нуклеотидів, яке здатне обмежити проліферативну активність лімфоцитів [35], а також генорегуляторні порушення в локусах імунорезистентності [45]. Тому ми вважаємо, що вищенаведені біохімічні зміни на тлі ГДФЦ є вкрай важливими в індукції механізмів порушення імунної системи організму-хазяїна.
A.A. Mauracher зі співавт. у систематичному огляді, який охоплює результати 186 наукових публікацій, виділяє патерн імунної дизрегуляції, характерний для первинних імунодефіцитів людини, що включає автоімунітет (64 %), кишковий синдром (38 %), лімфопроліферацію (36 %) та алергію (34 % випадків) [63].
Таким чином, формується важливе твердження: клінічно імунодефіцит у дітей з РАС проявляється у вигляді пентади імунозалежних церебральних та екстрацеребральних синдромів, що включає інфекційні, алергічні, імунозапальні, автоімунні та онкологічні прояви, які, згідно з постулатами клінічної імунології, є складовими фенотипу первинного імунодефіциту у людей.
На цьому факті ми хочемо зробити акцент і навести докази на користь того, що на тлі ГДФЦ формується специфічний імунний фенотип, якій варто розглядати не як наслідок або коморбідний стан при РАС та/або енцефалопатії, а як окрему нозологічну одиницю, генетичну хворобу, яку треба виділити і впровадити у клінічну практику поряд із іншими первинними імунодефіцитами. Для цього у табл. 1 продемонстрована подібність фенотипу ГДФЦ і первинного дефіциту манозозв’язувального лектину як приклад захворювання з переважним ураженням природженого імунітету, зумовленого патогенними поліморфними замінами нуклеотидів у гені MBL2.
/69_2.jpg)
У контексті розуміння ГДФЦ як самостійної генетичної хвороби людини правильніше говорити не про поліморфні варіанти генів циклу ензимів фолієвої кислоти, а про патогенні мутації, які призводять до чітко окреслених патологічних біохімічних, імунологічних, імунозапальних, інфекційних, автоімунних, нейровізуалізаційних та клінічних проявів [66]. Відповідно до цього, пацієнти із ГДФЦ потребують проведення імунотерапії для компенсації порушень імунного статусу, що доводить успішна апробація комбінованої імунотерапії Пропесом та Інфламафертином для усунення дефіцитів NK- та NKT-клітин, стану специфічного ГДФЦ-індукованого імунодефіциту, що є першим кроком до розробки ефективних імунотерапевтичних стратегій для зменшення клінічних проявів зниженої імунорезистентності та імунної дизрегуляції у дітей з РАС [59].
З огляду на імунокомпрометованість дітей з РАС, асоційованими з ГДФЦ, було встановлено, що для них є характерним специфічний мікробний спектр з переважанням інтрацелюлярних опортуністичних та умовно-патогенних вірусних, бактеріальних, грибкових та протозойних мікроорганізмів [4, 16, 46, 50, 70, 71, 78, 97]. Виділені чотири групи мікроорганізмів за частотою їх виявлення у дітей з РАС, асоційованими з ГДФЦ, мають бути враховані в алгоритмі етапного діагностичного мікробіологічного пошуку при плануванні послідовності дій при оцінці мікробного навантаження і визначенні потреби у призначенні протимікробних ліків [4]. За нашими спостереженнями, стрептококова інфекція була пов’язана з гіпо- і дисімуноглобулінемією, а також дефіцитом мієлопероксидази. Кандидоз був асоційований тільки з дефіцитом мієлопероксидази. Токсоплазмоз відзначався при дефіциті СD4+ Т-хелперів та комбінованих порушеннях імунітету. Наслідки природженої CMV-нейроінфекції мали місце тільки при комбінованих порушеннях імунітету [4].
Обґрунтування ролі інфекційного чинника у патогенезі хвороби при ГДФЦ створює передумови для апробації антимікробних стратегій лікування, призначених на підставі персоніфікованої оцінки мікробного профілю пацієнта. Відповідно до цього L.A. Snider зі співавт. здійснили подвійне сліпе плацебо-контрольоване рандомізоване клінічне випробування довготривалої профілактичної терапії пеніциліном VK у дозі 250 мг двічі на добу й азитроміцином у дозі 250 мг двічі на добу 1 раз на тиждень протягом 1 року при PANDAS (англ. Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal infections). Продемонстроване зниження частоти загострень стрептококової інфекції на 96 % і зменшення кількості рецидивів PANDAS на 61 % у пацієнтів, які приймали як пеніцилін, так і азитроміцин, порівняно з плацебо [94].
/68.jpg)
На сьогодні встановлено, що інфекційні агенти є активними компонентами патогенезу енцефалопатії у дітей з РАС. Мікроорганізми здатні як справляти прямі пошкоджуючі впливи на паренхіму головного мозку, так і бути залученими до непрямих імуноопосередкованих механізмів церебрального ураження шляхом індукції системного запалення та антимозкового автоімунітету [55, 68]. Прямий пошкоджуючий вплив інфекційних агентів може полягати в індукції енцефалітів і нейродегенеративних процесів [38, 42, 67, 91, 105]. Серед непрямих впливів інфекційних агентів на тканину ЦНС у дітей з РАС слід виділити принаймні два шляхи такого ураження. По-перше, мікроорганізми можуть бути тригерами антимозкового автоімунітету до мієліну [93] та нейронів різних структур головного мозку [22, 36, 40, 98]. За нашими даними, серологічні ознаки автоімунізації до автоантигенів підкіркових гангліїв півкуль великого мозку були асоційовані тільки із Streptococcus pyogenes та Borrelia, до нейронів мезолімбічної системи — EBV, HHV-6, HHV-7, Toxoplasma та TTV, до мієліну ЦНС — EBV, HHV-6, HHV-7, Borrelia та TTV, до ядер клітин сполучної тканини та поперечно-смугастих м’язів — EBV, HHV-6, HHV-7, Borrelia та TTV [7].
По-друге, інфекційні агенти в умовах імунної дизрегуляції можуть викликати стан системного запалення з індукцією гіперцитокінемії з нейротоксичним впливом [50, 62, 90], а також через вісь «мікробіота — кишечник — мозок» [11]. Посилюючи запалення в кишечнику, інфекційні агенти здатні індукувати подальше інтрацеребральне запалення у дітей з РАС шляхом аномального поширення запального процесу з інтестинального компартменту через кров і патологічно проникний гематоенцефалічний бар’єр до паренхіми головного мозку [11, 14].
Механізм розвитку і поширення запалення в організмі дітей з РАС, асоційованими з ГДФЦ, починаючи з дисбіозу кишечника і ураження кишкової стінки і закінчуючи інтрацеребральним запаленням з формуванням аберантних міжнейронних зв’язків у ЦНС, ми пропонуємо уявити у вигляді наступної схеми (рис. 3).
/69.jpg)
Оскільки імунні порушення на тлі ГДФЦ є ключовим компонентом імунопатогенезу енцефалопатії, очевидно, що відмінності у дефіцитах різних імунних чинників у пацієнтів з РАС, так звані імунні ендофенотипи, визначають тяжкість клінічного стану пацієнта і подальший перебіг хвороби [23, 44]. D.A. Bouboulis зі співавт. пропонують для такої енцефалопатії термін «інфекційно-індукована автоімунна енцефалопатія» (infection-induced autoimmune encephalopathy) [19]. Оскільки продемонстровано окремий імунозапальний шлях ураження ЦНС, не пов’язаний безпосередньо з автоімунною реакцією, на наш погляд, точнішим має бути термін «інфекційно-індукована запальна автоімунна енцефалопатія». Також можна запропонувати простіші і водночас більш ємні терміни — «імунозалежна енцефалопатія» або «ГДФЦ-індукована енцефалопатія».
За нашими даними, у пацієнтів з РАС, асоційованими з ГДФЦ, відзначається підвищення сироваткових концентрацій таких прозапальних показників, як ТМ2ПК, ФНП-альфа та ІЛ-6, що вказує на стан системного запалення в організмі цих дітей. Однак ці показники демонструють варіабельність за чутливістю, лабільністю і специфічністю, що передбачає необхідність комплексного аналізу даних [3]. Досліджувані показники асоційовані зі зростанням у сироватці крові індикаторів нейронального пошкодження НСЕ [56] і білка S-100 [109], що підтверджує уявлення щодо ролі системного запалення в індукції енцефалопатії у дітей з РАС, асоційованими з ГДФЦ, та відкриває шлях до апробації нових стратегій щодо антизапальної нейропротекторної терапії.
Справедливість запропонованої імунозалежної концепції формування енцефалопатії у дітей з РАС, асоційованими з ГДФЦ, підтверджується клінічною ефективністю імунотерапевтичних втручань, включаючи лікувальні підходи, спрямовані на досягнення нейропротекції через блокування інфекційних, автоімунних та імунозапальних шляхів ураження ЦНС. Зокрема, йдеться про застосування інфліксимабу (анти-ФНП-альфа-терапії) для пригнічення ФНП-альфа-індукованого системного запалення і пов’язаного з цим церебрального пошкодження [58], ритуксимабу (анти-СD20-терапії) для пригнічення антицеребрального автоімунітету та зумовленого цією автоагресією пошкодження нейронів ЦНС [1] та нормального в/в імуноглобуліну людини, який чинить інтегральну терапевтичну дію, гальмуючи всі імунозалежні механізми формування енцефалопатії, через протизапальні, антиінфекційні та імуномодулюючі властивості [8, 77, 86] (рис. 4).
/70.jpg)
Формулювання концепції ГДФЦ-індукованої енцефалопатії дозволяє об’єднати всі нейропсихіатричні синдроми в єдине ціле як різні прояви єдиної енцефалопатії зі спільним походженням. Ми вважаємо, що патогенетично не існує морбідних (РАС) та коморбідних (усі інші) психічних розладів, а є різні синдроми ГДФЦ-індукованої енцефалопатії зі спільним походженням, які дають цілісну картину ураження ЦНС у таких дітей (рис. 5). Крім того, у дітей з ГДФЦ-індукованою енцефалопатією відзначаються й екстрацеребральні прояви, такі як симптоми інфекцій [70], кишковий синдром [37], алергічні прояви [96], наслідки автоімунізації до позамозкових автоантигенів [68], онкологічні ураження [30], які іноді можуть бути тяжчими, ніж власне симптоми ураження ЦНС. Ці ознаки не вписуються в ізольовану клінічну картину діагнозу РАС. Отже, на основі власних спостережень та аналізу ми виявили, що в усіх без винятку дітей з РАС на тлі ГДФЦ відзначається ГДФЦ-індуковане мультиорганне полімодальне ураження, тобто патологія всього організму, а не тільки порушення психіки (рис. 5).
/70_2.jpg)
Отже, ми впевнені, що правильно розглядати цих пацієнтів як імунокомпрометованих осіб з гетерогенною за механізмом розвитку мультиорганною дисфункцією, а не як дітей з РАС, хоча саме поведінкові розлади можуть бути найбільш очевидними клінічними проявами при первинному огляді пацієнта.
Станом на сьогодні в Україні РАС у дітей є тяжкою соціальною, прогностично несприятливою інвалідизуючою патологією, що вважається невиліковною. Однак розробка дієвих способів лікування неможлива без поглиблення розуміння етіології і патогенезу хвороби. Тому, підсумовуючи усі наведені аргументи, ми маємо власний погляд на причини відсутності успішної терапії дітей із РАС. За нашими спостереженнями, усім пацієнтам ДГ був встановлений клінічний діагноз РАС, хоча власне ознаки аутизму у цих дітей були не єдиними проявами психоневрологічних розладів. У них відзначалися також когнітивні порушення, синдром дефіциту уваги і гіперактивності, обсесивно-компульсивний синдром, екстрапірамідні розлади, епілепсія, порушення харчової поведінки та ураження рухових провідникових нервових шляхів з відповідними нейровізуалізаційними проявами [2, 43, 61, 74].
Відсутність ретельного обстеження цих пацієнтів, а головне — відсутність аналізу причинно-наслідкових зв’язків та оцінки стану комплексу органів та систем, які неминуче мають структурно-функціональні ушкодження на тлі ГДФЦ, прирекли таких дітей на статус невиліковних із відсутністю навіть потенційної можливості полегшати їх стан за допомогою адекватної фармакологічної корекції. Ми вважаємо, що звуження клінічного діагнозу до РАС — це клінічна практика, яка не відповідає сучасному рівню знань і розуміння проблеми і не дозволяє відтворити цілісну картину ураження ЦНС у таких дітей, а отже, призначити адекватний набір лікувальних та реабілітаційних втручань.
D.A. Rossignol зі співавт. у систематичному огляді, присвяченому аналізу напрямків наукового пошуку етіології та патогенезу РАС у дітей, зазначають такі тренди останніх десятиріч, як виявлення у них типових змін: імунної дизрегуляції, запалення, оксидативного стресу, мітохондріальної дисфункції та токсичних впливів зовнішнього середовища, які комбінуються у варіабельній індивідуальній манері у кожного конкретного пацієнта [85], що обґрунтовує персоніфікований підхід до діагностики і лікування цього захворювання. Відповідно до цього R.E. Frye акумулював наукові докази доцільності персоніфікованого мультидисциплінарного підходу до дослідження та лікування дітей з РАС на підставі даних з ідентифікації індивідуального профілю механізмів церебрального та екстрацеребрального пошкодження в кожному конкретному випадку, що отримав назву BaS-BISTOR [35]. Зазначений підхід значною мірою відповідає запропонованому алгоритму діагностики та лікування згідно з даною науковою концепцією.
Пропонована нами концепція ГДФЦ як самостійної хвороби у дітей дозволяє об’єднати в єдине ціле на перший погляд різнорідні церебральні і екстрацеребральні порушення, які мають спільне походження і вимагають реалізації узгоджених моніторингу й прогнозування, терапевтичних та реабілітаційних програм у психіатричній практиці. Формування погляду на ГДФЦ як на етіологічний чинник комплексу пов’язаних між собою біохімічних та імунозалежних уражень дозволяє здійснювати синтетичний, а не механістичний підхід до клінічного ведення пацієнта, що базується на розумінні проблеми і обґрунтуванні діагностично-лікувальних втручань, які раніше не розглядалися у таких випадках.
Важливо пам’ятати, що за останні 30 років у світі відзначається стрімке зростання поширеності розладів спектра аутизму в дитячій популяції. Так, частота цієї патології зросла за окреслений період щонайменше в 200 разів, що дозволяє говорити про феномен «цунамі» дитячого аутизму у сучасному світі [35].
Таке стрімке погіршення психологічного статусу дітей можна також пояснити, спираючись на концепцію ГДФЦ як головний чинник виникнення аутизму. Відомо, що поліморфізми генів основних ферментів фолатного циклу доволі поширені в сучасній популяції. Носієм хоча б однієї такої патогенної заміни зараз є кожен третій житель Землі. На жаль, маємо констатувати, що протягом останніх десятиріч мимоволі створені умови для посилення пенетрантності ГДФЦ, чим можна пояснити неухильне зростання частоти РАС. До цих причин можна віднести підвищення витривалості сучасних людей через покращення умов життя та якості медичних послуг, що зменшує дію природного добору, перемішування різних етносів, що забезпечує міграцію ГДФЦ із азійських до інших популяцій, збільшення частки породіль пізнього віку, що зумовлює реалізацію материнсько-плодових імунних конфліктів [21]. Створення великих мегаполісів становить сприятливі умови для поширення опортуністичних та умовно-патогенних інфекцій, погіршення екологічних умов, що поглиблює ГДФЦ-індуковану імуносупресію та сприяє інтоксикацїї головного мозку важкими металами, збільшення темпу життя та стресових навантажень на організм сучасної людини, погіршення якості харчових продуктів тощо [51]. Зважаючи на всі наведені вище чинники, можна очікувати тільки подальшого зростання частоти РАС у дітей у майбутньому, оскільки потенціал ГДФЦ як причини таких порушень на сьогодні не вичерпаний. Це обґрунтовує необхідність розробки профілактичних заходів для нівелювання патогенної дії ГДФЦ на здоров’я дитячої популяції.
Ми впевнені, що результати, отримані під час даного дослідження, так само як і низки інших праць в царині нейроімунології РАС, надають ефективні інструменти запобігання ГДФЦ і зменшення її негативного впливу на сучасну людину, що дозволяє з певним оптимізмом дивитися на перспективу подолання загрозливої тенденції стрімкого зростання частоти тяжких нейропсихіатричних порушень серед дітей.
Висновок
За результатами власних спостережень, комплексного аналізу та синтезу лабораторних даних із клінічним перебігом стану дітей з діагнозом РАС, а також даних сучасних досліджень авторитетних світових шкіл, нами сформована концепція ГДФЦ-індукованої енцефалопатії:
— Генетично детермінований комплекс мутації основних генів фолатного циклу у дітей формує специфічний фенотип, якій варто розглядати як генетичну хворобу, окрему нозологічну одиницю — генетичний дефіцит фолатного циклу. Для пацієнтів з ГДФЦ є характерним патерн біохімічних змін у вигляді гіпергомоцистеїнемії, дефіциту вітамінів (В6, В9, В12, D3), гіперкреатинінемії, підвищення лактатдегідрогенази, креатинфосфокінази та первинного імунодефіциту з переважним ураженням природженого імунітету, який є основою імунозапальних, інфекційних, автоімунних, нейровізуалізаційних та клінічних проявів.
— Ключовим наслідком ГДФЦ-індукованого імунного дисбалансу є енцефалопатія, яка об’єднує в єдине ціле психічні та неврологічні розлади у дітей та екстрацеребральні прояви, такі як симптоми інфекцій, кишковий синдром, алергічні прояви, наслідки автоімунізації до позамозкових автоантигенів, онкологічні ураження, які можуть бути тяжчими, ніж власне симптоми ураження ЦНС.
— Звуження характеристики психічних розладів у дітей із ГДФЦ до діагнозу РАС є помилковим і потребує проведення подальшого обстеження та ретельного діагностичного пошуку, оскільки у цих пацієнтів існує етіологічне та патогенетичне підґрунтя для мультиорганного полімодального ураження.
— Комплексна діагностика ГДФЦ у дітей із церебральними та екстрацеребральними проявами надає підставу пропонувати впровадження у клінічну практику поряд з реабілітаційними програмами обґрунтовані патогенетичні схеми лікування дітей із РАС, які в кожному окремому напрямку довели свою ефективність.
Конфлікт інтересів. Автори заявляють про відсутність конфлікту інтересів та власної фінансової зацікавленості при підготовці даної статті.
Отримано/Received 20.05.2022
Рецензовано/Revised 31.05.2022
Прийнято до друку/Accepted 14.06.2022
Список литературы
1. Мальцев Д.В. Ефективність ритуксимабу при розладах спектра аутизму, асоційованих із генетичним дефіцитом фолатного циклу, з ознаками антинейронального автоімунітету. Міжнародний неврологічний журнал. 2021. Т. 17(5). С. 10-17.
2. Мальцев Д.В. Нейрорадіологічні ознаки енцефалопатії у дітей з розладами спектра аутизму, асоційованими з генетичним дефіцитом фолатного циклу. Український неврологічний журнал. 2021. Т. 3. С. 16-30.
3. Мальцев Д.В. Оцінка маркерів запалення та нейронального пошкодження у пацієнтів з розладами спектра аутизму, асоційованими з генетичним дефіцитом фолатного циклу. Імунологія та алергологія: наука і практика. 2021. Т. 3. С. 31-39.
4. Мальцев Д.В. Результати вивчення мікробного спектра у дітей з розладами спектра аутизму, асоційованими з генетичним дефіцитом фолатного циклу. Чоловіче здоров’я. Гендерна медицина. 2021. Т. 2. С. 26-39.
5. Мальцев Д.В. Результати вивчення показників біохімічного профілю у дітей з розладами спектра аутизму, асоційованими з генетичним дефіцитом фолатного циклу. Імунологія та алергологія: наука і практика. 2021. Т. 1–2. С. 19-28.
6. Мальцев Д.В. Результати оцінки імунного статусу у дітей з розладами спектра аутизму: імунодефіцит, асоційований з генетичним дефіцитом фолатного циклу. Імунологія та алергологія: наука і практика. 2021. Т. 4. P. 5-23.
7. Мальцев Д.В. Результати пошуку лабораторних ознак автоімунних реакцій до мозкових та позамозкових автоантигенів у дітей з розладами спектра аутизму, асоційованими з генетичним дефіцитом фолатного циклу. Мedical science of Ukraine. 2021. Т. 17(3). С. 22-37.
8. Мальцев Д.В. Результати ретроспективного аналізу застосування нормального внутрішньовенного імуноглобуліну людини у високій дозі для лікування імунозалежної енцефалопатії з клінічною картиною розладів аутистичного спектра в дітей з генетичним дефіцитом фолатного циклу. Міжнародний неврологічний журнал. 2021. Т. 17(8). С. 31-43.
9. Asogwa K., Buabeng K., Kaur A. Psychosis in a 15-Year-Old Female with Herpes Simplex Encephalitis in a Background of Mannose-Binding Lecithin Deficiency. Case Rep. Psychiatry. 2017. Vol. 2017. P. 1429847.
10. Aydin S.Z., Atagunduz P., Inanc N. et al. Mannose binding lectin levels in spondyloarthropathies. J. Rheumatol. 2007. Vol. 34(10). P. 2075-2077.
11. Azhari A., Azizan F., Esposito G. A systematic review of gut-immune-brain mechanisms in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Dev. Psychobiol. 2019. Vol. 61(5). P. 752-771. doi: 10.1002/dev.21803.
12. Badiga S., Johanning G.L., Macaluso M. et al. A lower degree of PBMC L1 methylation in women with lower folate status may explain the MTHFR C677T polymorphism associated higher risk of CIN in the US post folic acid fortification era. PLoS One. 2014. Vol. 9(10). e110093.
13. Bagheri-Hosseinabadi Z., Imani D., Yousefi H., Abbasifard M. MTHFR gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis based on 16 studies. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020. Vol. 39(8). P. 2267-2279.
14. Baj J., Sitarz E., Forma A. et al. Alterations in the Nervous System and Gut Microbiota after beta-Hemolytic Streptococcus Group A Infection-Characteristics and Diagnostic Criteria of PANDAS Re-cognition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020. Vol. 21(4). P. 1476. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041476.
15. Belardo A., Gevi F., Zolla L. et al. The concomitant lower concentrations of vitamins B6, B9 and B12 may cause methylation deficiency in autistic children. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019. Vol. 70. P. 38-46.
16. Binstock T. Intra-monocyte pathogens delineate autism subgroups. Med. Hypotheses. 2001. Vol. 56(4). P. 523-531.
17. Birbian N., Singh J., Jindal S.K. et al. Association of the wild-type A/A genotype of MBL2 codon 54 with asthma in a North Indian population. Dis. Markers. 2012. Vol. 32(5). Р. 301-308.
18. Borges M.C., Hartwig F.P., Oliveira I.O., Horta B.L. Is there a causal role for homocysteine concentration in blood pressure? A Mendelian randomization study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016. Vol. 103(1). P. 39-49.
19. Bouboulis D.A., Mast P.A. Infection-Induced Autoimmune Encephalopathy: Treatment with Intravenous Immune Globulin Therapy. A Report of Six Patients. Int. J. Neurol. Res. 2016. Vol. 2. P. 256-258.
20. Boughrara W., Aberkane M., Fodil M. et al. Impact of –MTHFR rs1801133, MTHFR rs1801131 and ABCB1 rs1045642 polymorphisms with increased susceptibility of rheumatoid arthritis in the West Algerian population: A case-control study. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2015. Vol. 40(4). P. 363-371.
21. Brimberg L., Sadiq A., Gregersen P.K., Diamond B. Brain-reactive IgG correlates with autoimmunity in mothers of a child with an autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Psychiatry. 2013. Vol. 18(11). P. 1171-1177.
22. Cabanlit M., Wills S., Goines P. et al. Brain-specific autoantibodies in the plasma of subjects with autistic spectrum disorder. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007. Vol. 107. P. 92-103.
23. Careaga M., Rogers S., Hansen R.L. et al. Immune endophenotypes in children with autism spectrum disorder. Biol. Psychiatry. 2017. Vol. 81. 434-441.
24. Carlus S.J., Abdallah A.M., Bhaskar L.V. et al. The MTHFR C677T polymorphism is associated with mitral valve rheumatic heart disease. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016. Vol. 20(1). Р. 109-114.
25. Chen F., Wen T., Lv Q., Liu F. Associations between Folate Metabolism Enzyme Polymorphisms and Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Cancer. 2020. Vol. 72(7). P. 1211-1218.
26. Chen H., Yang X., Lu M. et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphisms and recurrent pregnancy loss in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2016. Vol. 293(2). P. 283-290.
27. Chen L., Shi X.J., Liu H. et al. Oxidative stress marker aberrations in children with autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 87 studies (N = 9109). Transl. Psychiatry. 2021. Vol. 11(1). P. 15.
28. Chen N., Zhang X., Zheng K. et al. Increased risk of group B Streptococcus causing meningitis in infants with mannose-binding lectin deficiency. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019. Vol. 25(3). 384.e1-384.e3.
29. Christiansen O.B., Kilpatrick D.C., Souter V. et al. Mannan-binding lectin deficiency is associated with unexplained recurrent miscarriage. Scand. J. Immunol. 1999. Vol. 49(2). P. 193-196.
30. Crawley J.N., Heyer W.D., LaSalle J.M. Autism and Cancer Share Risk Genes, Pathways, and Drug Targets. Trends Genet. 2016. Vol. 32(3). P. 139-146.
31. Dimitroulas T., Sandoo A., Hodson J. et al. Associations between asymmetric dimethylarginine, homocysteine, and the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism (rs1801133) in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2016. Vol. 45(4). P. 267-273.
32. El-Hadidy M.A., Abdeen H.M., Abd El-Aziz S.M., Al-Harrass M. MTHFR gene polymorphism and age of onset of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014. Vol. 2014. P. 318483.
33. Foldager L., Köhler O., Steffensen R. et al. Bipolar and panic disorders may be associated with hereditary defects in the innate immune system. J. Affect Disord. 2014. Vol. 164. P. 148-154.
34. Frustaci A., Neri M., Cesario A. et al. Oxidative stress-rela-ted biomarkers in autism: systematic review and meta-analyses. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012. Vol. 52(10). P. 2128-2141.
35. Frye R.E. A Personalized Multidisciplinary Approach to Evaluating and Treating Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Pers. Med. 2022. Vol. 12(3). P. 464.
36. Frye R.E., Sequeira J.M., Quadros E.V. et al. Cerebral folate receptor autoantibodies in autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Psychiatry. 2013. Vol. 18(3). P. 369-381.
37. Furlano R.I., Anthony A., Day R. et al. Colonic CD8 and gamma delta T-cell infiltration with epithelial damage in children with autism. J. Pediatr. 2001. Vol. 138(3). P. 366-372.
38. Ghaziuddin M., Al-Khouri I., Ghоaziuddin N. Autistic symptoms following herpes encephalitis. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry. 2002. Vol. 11(3). P. 142-146.
39. Glesse N., Monticielo O.A., Mattevi V.S. et al. Association of mannose-binding lectin 2 gene polymorphic variants with susceptibility and clinical progression in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011. Vol. 29(6). P. 983-990.
40. González-Toro M.C., Jadraque-Rodríguez R., Sempere-Pérez Á. et al. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: two paediatric cases. Rev. Neurol. 2013. Vol. 57(11). P. 504-508.
41. Guo B.Q., Li H.B., Ding S.B. et al. Blood homocysteine levels in children with autism spectrum disorder: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2020. Vol. 291. P. 113283.
42. Harberts E., Yao K., Wohler J.E. et al. Human herpesvirus-6 entry into the central nervous system through the olfactory pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011. Vol. 108(33). P. 13734-9.
43. Hardan A.Y., Fung L.K., Frazier T. et al. A proton spectro-scopy study of white matter in children with autism. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2016. Vol. 66. P. 48-53.
44. Heuer L., Ashwood P., Schauer J. et al. Reduced Levels of Immunoglobulin in Children With Autism Correlates With Behavioral Symptoms. Autism. Res. 2008. Vol. 1(5). P. 275-283.
45. Horiuchi F., Yoshino Y., Kumon H. et al. Identification of aberrant innate and adaptive immunity based on changes in global gene expression in the blood of adults with autism spectrum disorder. J. Neuroinflammation. 2021. Vol. 18(1). P. 102.
46. Hughes H.K., Ashwood P. Anti-Candida albicans IgG Antibodies in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front. Psychiatry. 2018. Vol. 26(9). P. 627. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00627.
47. Hughes H.K., Ko E.M., Rose D., Ashwood P. Immune Dysfunction and Autoimmunity as Pathological Mechanisms in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. Vol. 12. P. 405.
48. Jin Z., Ji Z., Hu J. Mannose-binding lectin gene site mutations and the susceptibility of rheumatic heart disease. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2001. Vol. 81(21). P. 1284-1286.
49. Kovacs M., Papp M., Lakatos P.L. et al. Low mannose-bin-ding lectin (MBL) is associated with paediatric inflammatory bowel diseases and ileal involvement in patients with Crohn disease. J. Crohns Colitis. 2013. Vol. 7(2). P. 134-141.
50. Lecointe D., Fabre M., Habes D. et al. Macrophage activation syndrome in primary human herpes virus-6 infection: a rare condition after liver transplantation in infants. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2000. Vol. 24(12). P. 1227-1228.
51. Ledda C., Cannizzaro E., Lovreglio P. et al. Exposure to Toxic Heavy Metals Can Influence Homocysteine Metabolism? Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. Vol. 9(1). P. 30.
52. Li C., Yichao J., Jiaxin L. et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism and risk of chronic myelogenous leukemia: a meta-analysis. J. BUON. 2015. Vol. 20(6). Р. 1534-1545.
53. Li M., Tang Y., Zhao E.Y. et al. Relationship between MTHFR gene polymorphism and susceptibility to bronchial asthma and glucocorticoid efficacy in children. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2021. Vol. 23(8). P. 802-808.
54. Li Y., Qiu S., Shi J. et al. Association between MTHFR C677T/A1298C and susceptibility to autism spectrum disorders: a meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2020. Vol. 20(1). P. 449.
55. Li Ye., Viscidi R.P., Kannan G. et al. Chronic Toxoplasma gondii Infection Induces Anti-N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Auto-antibodies and Associated Behavioral Changes and Neuropatho-logy. Infect. Immun. 2018. Vol. 86(10). e00398-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00398-18.
56. Lv M.N., Zhang H., Shu Y. et al. The neonatal levels of TSB, NSE and CK-BB in autism spectrum disorder from Southern China. Transl. Neurosci. 2016. Vol. 7(1). P. 6-11.
57. Madsen H.O., Videm V., Svejgaard A. et al. Association of mannose-binding-lectin deficiency with severe atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1998. Vol. 352. P. 959-960.
58. Maltsev D., Natrus L. The effectiveness of infliximab in autism spectrum disorders associated with folate cycle genetic deficiency. Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Clinical Psychologythis. 2020. Vol 11(3). P. 583-594.
59. Maltsev D.V., Stefanyshyn V.M. Efficacy of combined immunotherapy with propes and inflamafertin in selective deficiency of nk and nkt cells in children with autism spectrum disorders associated with genetic deficiency of the folate cycle. Current Pediatric Research. 2021. Vol. 25(4). P. 536-540.
60. Mao N., Chen J., Wang J. et al. Correlations of Methylen-etetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene Polymorphism and Genomic DNA Hypomethylation Level with Ankylosing Spondylitis. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2020. Vol. 42(3). P. 307-312.
61. Marseglia L.M., Nicotera A., Salpietro V. et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia and MTHFR polymorphisms as antenatal risk factors of white matter abnormalities in two cohorts of late preterm and full term newborns. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015. Vol. 2015. P. 543134. doi: 10.1155/2015/543134.
62. Masi A., Quintana D.S., Glozier N. et al. Cytokine aberrations in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry. 2015. Vol.20(4). P. 440-446.
63. Mauracher A., Gujer E., Bachmann L.M. Patterns of Immune Dysregulation in Primary Immunodeficiencies: A Systematic Review. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021. Vol. 9(2). P. 792-802.
64. Mohammad N.S., Shruti P.S., Bharathi V. et al. Clinical utility of folate pathway genetic polymorphisms in the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders. Psychiatr. Genet. 2016. Vol. 26(6). P. 281-286.
65. Molina-López J., Leiva-García B., Planells E., Planells P. Food selectivity, nutritional inadequacies, and mealtime behavioral problems in children with autism spectrum disorder compared to neurotypical children. Int. J. Eat Disord. 2021. Oct 27. Online ahead of print.
66. Moll S., Varga E.A. Homocysteine and MTHFR Mutations. Circulation. 2015. Vol. 132(1). e6-9.
67. Monge-Galindo L., Pérez-Delgado R., López-Pisón J. et al. Mesial temporal sclerosis in paediatrics: its clinical spectrum. Our experience gained over a 19-year period. Rev. Neurol. 2010. Vol. 50(6). P. 341-348.
68. Mostafa G.A., El-Sherif D.F., Al-Ayadhi L.Y. et al. Systemic auto-antibodies in children with autism. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014. Vol. 272(1-2). P. 94-8.
69. Naghibalhossaini F., Ehyakonandeh H., Nikseresht A., Kamali E. Association Between MTHFR Genetic Variants and Multiple Sclerosis in a Southern Iranian Population. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2015. Vol. 4(2). P. 87-93.
70. Nayeri T., Sarvi S., Moosazadeh M. et al. Relationship between toxoplasmosis and autism: A systematic review and meta-ana-lysis. Microb. Pathog. 2020. Vol. 147. P. 104434.
71. Nicolson G.L., Gan R., Nicolson N.L., Haier J. Evidence for Mycoplasma ssp., Chlamydia pneunomiae, and human herpes virus-6 coinfections in the blood of patients with autistic spectrum disorders. J. Neurosci Res. 2007. Vol. 85(5). P. 1143-1148.
72. Nisihara R.M., Utiyama S.R., Oliveira N.P., Messias-Reason I.J. Mannan-binding lectin deficiency increases the risk of recurrent infections in children with Down’s syndrome. Hum. Immunol. 2010. Vol. 71(1). P. 63-66.
73. Ohlenschlaeger T., Garred P., Madsen H.O., Jacobsen S. Mannose-binding lectin variant alleles and the risk of arterial thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. New Eng. J. Med. 2004. Vol. 351. P. 260-267.
74. Pavone V., Praticò A.D., Parano E. et al. Spine and brain malformations in a patient obligate carrier of MTHFR with autism and mental retardation. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2012. Vol. 114(9). P. 1280-1282.
75. Peerbooms O.L., van Os J., Drukker M. et al. Meta-analysis of MTHFR gene variants in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and unipolar depressive disorder: evidence for a common genetic vulnerability? Brain. Behav. Immun. 2011. Vol. 25(8). P. 1530-1543.
76. Peng Q., Lao X., Huang X. et al. The MTHFR C677T polymorphism contributes to increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease: evidence based on 40 case-control studies. Neurosci. Lett. 2015. Vol. 586. P. 36-42.
77. Perlmutter S.J., Leitman S.F., Garvey M.A. et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange and intravenous immunoglobulin for obsessive-compulsive disorder and tic disorders in childhood. Lancet. 1999. Vol. 354(9185). P. 1153-1158.
78. Pinillos-Pisón R., Llorente-Cereza M.T., López-Pisón J. Congenital infection by cytomegalovirus. A review of our 18 years’ experience of diagnoses. Rev. Neurol. 2009. Vol. 48(7). P. 349-353.
79. Promthet S., Pientong C., Ekalaksananan T. et al. Risk factors for rectal cancer and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphisms in a population in Northeast Thailand. Asian. Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012. Vol. 13(8). P. 4017-4023.
80. Pu D., Shen Y., Wu J. Association between MTHFR gene polymorphisms and the risk of autism spectrum disorders: a meta-analysis. Autism Res. 2013. Vol. 6(5). P. 384-392.
81. Qi X., Sun X., Xu J. et al. Associations between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphisms and hepatocellular carcinoma risk in Chinese population. Tumour. Biol. 2014. Vol. 35(3). P. 1757-1762.
82. Rai V. Association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene C677T polymorphism with autism: evidence of genetic susceptibility. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016. Vol. 31(4). P. 727-735.
83. Rai V., Yadav U., Kumar P. et al. Maternal methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism and down syndrome risk: a meta-analysis from 34 studies. PLoS One. 2014. Vol. 9(9). e108552.
84. Rossignol D.A., Frye R.E. The Effectiveness of Cobalamin (B12) Treatment for Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2021. Vol. 11(8). P. 784.
85. Rossignol D.A., Frye R.E. A review of research trends in physiological abnormalities in autism spectrum disorders: immune dysregulation, inflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and environmental toxicant exposures. Mol. Psychiatry. 2012. Vol. 17. P. 389-401.
86. Rossignol D.A., Frye RE. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Immunoglobulin G Abnormalities and the Therapeutic Use of Intravenous Immunoglobulins (IVIG) in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Pers. Med. 2021. Vol. 11(6). P. 488.
87. Russo A.J., Krigsman A., Jepson B., Wakefield A. Low serum myeloperoxidase in autistic children with gastrointestinal disease. Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology. 2009. Vol. 2. P. 85-94.
88. Sadeghiyeh T., Dastgheib S.A., Mirzaee-Khoramabadi K. et al. Association of MTHFR 677C>T and 1298A>C polymorphisms with susceptibility to autism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2019. Vol. 46. P. 54-61.
89. Saevarsdottir S., Vikingsdottir T., Vikingsson A. et al. Low mannose binding lectin predicts poor prognosis in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. A prospective study. J. Rheumatol. 2001. Vol. 28(4). P. 728-734.
90. Saghazadeh A., Ataeinia B., Keynejad K. A meta-analysis of pro-inflammatory cytokines in autism spectrum disorders: Effects of age, gender, and latitude. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019. Vol. 115. P. 90-102.
91. Sakamoto A., Moriuchi H., Matsuzaki J. et al. Retrospective diagnosis of congenital cytomegalovirus infection in children with autism spectrum disorder but no other major neurologic deficit. Brain. Dev. 2015. Vol. 37(2). P. 200-205.
92. Singh A., Pandey S., Pandey L.K., Saxena A.K. In human alleles specific variation of MTHFR C677T and A1298C associated "risk factor" for the development of ovarian cancer. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2015. Vol. 11(1). P. 67-70.
93. Singh V.K., Warren R.P., Odell J.D. et al. Antibodies to myelin basic protein in children with autistic behavior. Brain. Behav. Immun. 1993. Vol. 7(1). P. 97-103.
94. Snider L.A., Lougee L., Slattery M. et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis with azithromycin or penicillin for childhood-onset neuropsychiatric disorders. Biol. Psychiatry. 2005. Vol. 57(7). P. 788-792.
95. Swierzko A.S., Szala A., Sawicki S. et al. Mannose-Binding Lectin (MBL) and MBL-associated serine protease-2 (MASP-2) in women with malignant and benign ovarian tumours. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014. Vol. 63(11). P. 1129-1140.
96. Theoharides T.C., Tsilioni I., Patel A.B., Doyle R. Atopic diseases and inflammation of the brain in the pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorders. Transl. Psychiatry. 2016. Vol. 6(6). e844.
97. Valayi S., Eftekharian M.M., Taheri M., Alikhani M.Y. Evaluation of antibodies to cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus in patients with autism spectrum disorder. Hum. Antibodies. 2017. Vol. 26(3). P. 165-169.
98. Venâncio P., Brito M.J., Pereira G., Vieira J.P. Anti-N-me-thyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis with positive serum antithyroid antibodies, IgM antibodies against mycoplasma pneumoniae and human herpesvirus 7 PCR in the CSF. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014. Vol. 33 (8). P. 882-883.
99. Wan L., Li Y., Zhang Z., Sun Z. et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and psychiatric diseases. Transl. Psychiatry. 2018. Vol. 8(1). P. 242.
100. Wang T., Zhang H.P., Zhang X. et al. Is Folate Status a Risk Factor for Asthma or Other Allergic Diseases? Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2015. Vol. 7(6). P. 538-546.
101. Wang Y., Yang H., Duan G. et al. MTHFR gene A1298C polymorphisms are associated with breast cancer risk among Chinese population: evidence based on an updated cumulative meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015. Vol. 8(11). Р. 20146-20156.
102. Wang Z., Ding R., Wang J. et al. The Association between Vitamin D Status and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2020. Vol. 13(1). E86.
103. Warren R.P., Margaretten N.C., Foster A. Reduced natural killer cell activity in autism. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry. 1987. Vol. 26. P. 333-335.
104. Warren R.P., Yonk L.J., Burger R.A. et al. Deficiency of suppressor inducer T cells in autism. Immunol. Invest. 1990. Vol. 19. P. 245-251.
105. Wipfler P., Dunn N., Beiki O. et al. The Viral Hypothesis of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy — Is Human Herpes Virus-6 the Missing Link? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Seizure. 2018. Vol. 54. P. 33-40.
106. Yang Y., Luo Y., Yuan J. et al. Association between maternal, fetal and paternal MTHFR gene C677T and A1298C polymorphisms and risk of recurrent pregnancy loss: a comprehensive evaluation. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2016. Vol. 293(6). P. 1197-1211.
107. Yektaş Ç., Alpay M., Tufan A.E. et al. Comparison of serum B12, folate and homocysteine concentrations in children with autism spectrum disorder or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and healthy controls. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019. Vol. 15. P. 2213-2219.
108. Yigit S., Inanir A., Tural S. et al. The effect of IL-4 and MTHFR gene variants in ankylosing spondylitis. Z. Rheumatol. 2015. Vol. 74(1). P. 60-66.
109. Zheng Z., Zheng P., Zou X. et al. Peripheral Blood S100B Levels in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Autism. Dev. Disord. 2020. Vol. 51(8). P. 2569-2577.
/67.jpg)
/68.jpg)
/69.jpg)
/70.jpg)

/69_2.jpg)
/70_2.jpg)