Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 18, №1, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Протизапальний вплив miR-148a грудного молока на стан слизових оболонок у недоношених новонароджених дітей
Авторы: O.E. Abaturov (1), A.O. Tovarnytska (2)
(1) — Dnipro State Medical University, Dnipro, Ukraine
(2) — Dnipro Medical Institute of Traditional and Non-Traditional Medicine, Dnipro, Ukraine
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
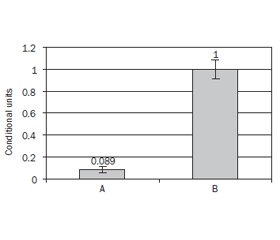
Актуальність. Грудне молоко (ГМ) — оптимальний продукт харчування для новонароджених, джерело екзогенних мікроРНК (miR). Одним з представників висококонцентрованого пулу miR ГМ є miR-148a. Сьогоднi бракує даних про вплив miR-148a на розвиток некротизуючого ентероколіту (НЕК) у недоношених новонароджених дітей. Мета дослідження: вивчити вплив miR-148a ГМ матері на ймовірність розвитку НЕК у недоношених новонароджених дітей. Матеріали та методи. Oбстежено 74 новонароджених, які проходили лікування в неонатальних відділеннях. Bизначено рівень miR-148а в ГМ 44 матерів новонароджених дітей, які перебували на виключно грудному вигодовуванні (ГВ). Паралельно проводилося визначення експресії генів фактора транскрипції T-bet у клітинах зіскрібка букальної слизової оболонки всіх новонароджених. Було виділено три групи порівняння: першу становили 32 новонароджені до 37 тижнів гестації на ГВ, другу — 30 недоношених новонароджених на штучному вигодовуванні, контрольну — 12 доношених новонароджених на ГВ. Результати. Медіана гестаційного віку дітей 1-ї групи становила 33 (31; 34) тижні, 2-ї — 32,5 (32; 35) тижня і порівняно вищою була в групі контролю (р < 0,001) — 40 (39; 41) тижнів. Неонатальна енцефалопатія як основний діагноз зустрічалася частіше серед доношених новонароджених (р < 0,001). Діти 1-ї та 2-ї груп суттєво не відрізнялися за частотою випадків респіраторного дистрес-синдрому, неонатальної енцефалопатії (р > 0,05). У 2-й групі порівняно з 1-ю вірогідно частіше (р < 0,05) зустрічалися прояви НЕК: 9/30,0 ± 8,4 % проти 3/9,4 ± 5,2 %. Виявлено, що рівень експресії miR-148a в ГМ матерів недоношених дітей на ГВ був вірогідно нижчий (р < 0,001), ніж у групі доношених: 0,089 (0,048; 0,142) ум.од. проти 1,0 (1,0; 1,0) ум.од. Рівень експресії фактора транскрипції T-bet у клітинах зіскрібка букальної слизової оболонки був вищий у недоношених дітей із клінікою НЕК (р = 0,022): 2,36 (1,94; 3,17) ум.од. проти 1,49 (1,0; 3,27) ум.од. у дітей без ознак НЕК. Доведено наявність прямого зв’язку між рівнем T-bet і проявами НЕК (r = 0,271; р = 0,021) та визначено зворотний кореляційний зв’язок між рівнем експресії miR-148a в ГМ матері та рівнем експресії T-bet (r = –0,371; p = 0,043). Висновки. У ГМ матерів, діти яких народилися передчасно і мають проблеми з адаптацією, рівень експресії miR-148a відносно нижчий, ніж у матерів, які народили в строк. При розвитку НЕК спостерігається підвищення рівня miR-148a в ГМ матері, що сприяє зниженню експресії T-bet слизових оболонок дитини і чинить протекторний вплив на стінки кишечника.
Background. Breast milk (BM) is an optimal nutritional product for newborns and a source of exogenous microRNAs (miR). MiR-148a is one of the most highly expressed miR of BM. Currently, there is a lack of data on the miR-148a effect on the development of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in premature newborns. The purpose of the study was to determine the influence of miR-148a of the mother’s BM on the risk of NEC development in preterm newborns. Materials and methods. We examined 74 newborns, who were treated in neonatal departments. We determined the level of miR-148a in the BM of 44 mothers of exclusively breastfed children. In parallel, we evaluated gene expression of the transcription factor T-bet in scrapings of the buccal mucosa of all the newborns. Three groups for comparison were selected: group 1 consisted of 32 newborns up to 37 weeks of gestation on breastfeeding (BF); group 2 — of 30 preterm newborns on artificial feeding; the control group — 12 full-term newborns on BF. Results. The gestational age median of group 1 children was 33 (31; 34) weeks; group 2 — 32.5 (32; 35) weeks; and it was comparatively higher in the control group (p < 0.001) — 40 (39; 41) weeks. Neonatal encephalopathy as the main diagnosis occurred more often among full-term newborns (p < 0.001). Children of groups 1 and 2 did not differ significantly in the frequency of cases of respiratory distress syndrome and neonatal encephalopathy (p > 0.05). In group 2 compared to the first one, manifestations of NEC occurred significantly more often (p < 0.05): 9/30.0 ± 8.4 % vs 3/9.4 ± 5.2 %. We determined that the level of miR-148a expression in the BM of the mothers of premature children on BF was significantly lower (p < 0.001) than in the group of full-term children: 0.089 (0.048; 0.142) c.u. vs 1.0 (1.0; 1.0) c.u. Furthermore, the level of the transcription factor T-bet expression in the cells of the buccal mucosa scrapings was higher in premature children with clinical NEC (p = 0.022): 2.36 (1.94; 3.17) c.u. vs 1.49 (1.0; 3.27) c.u. in children without signs of NEC. We proved the presence of direct positive correlation between the T-bet level and NEC manifestations (r = 0.271; p = 0.021) and determined the inverse correlation between the level of miR-148a expression in the mother’s BM and the level of T-bet expression (r = –0.371; p = 0.043). Conclusions. The miR-148a expression level is relatively lower in the BM of the mothers whose children were born prematurely and have problems with adaptation than in the mothers who gave birth at term. However, in case of NEC development, there is an increase of miR-148a level in the mother’s BM, which contributes to a decrease in the T-bet expression in the mucous membranes of the child and has a protective impact on intestinal walls.
miR-148a; T-bet; недоношені; новонароджені; некротизуючий ентероколіт
miR-148a; T-bet; preterm infants; premature newborns; necrotizing enterocolitis
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Hatmal M.M., Al-Hatamleh M.A.I., Olaimat A.N. et al. Immunomodulatory Properties of Human Breast Milk: MicroRNA Contents and Potential Epigenetic Effects. Biomedicines. 2022 May 24. 10(6). 1219. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061219.
- Infant and Young Child Nutrition: Global Strategy on Infant and Young Child Feeding. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/infant-and-young-child-feeding.
- Yi D.Y., Kim S.Y. Human Breast Milk Composition and Function in Human Health: From Nutritional Components to Microbiome and –MicroRNAs. Nutrients. 2021 Sep 2. 13(9). 3094. doi: 10.3390/nu13093094.
- Vélez-Ixta J.M., Benítez-Guerrero T., Aguilera-Hernández A. et al. Detection and Quantification of Immunoregulatory miRNAs in Human Milk and Infant Milk Formula. BioTech (Basel). 2022 Apr 20. 11(2). 11. doi: 10.3390/biotech11020011.
- Jiang X., You L., Zhang Z. et al. Biological Properties of Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Physiological Functions in Infant. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021 Jun 25. 9. 693534. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.693534.
- Manca S., Upadhyaya B., Mutai E. et al. Milk exosomes are bioavailable and distinct microRNA cargos have unique tissue distribution patterns. Sci. Rep. 2018 Jul 27. 8(1). 11321. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29780-1.
- Абатуров О.Є., Товарницька А.О. Вплив miR-155 грудного молока на стан здоров’я недоношених новонароджених. Здоров’я дитини. 2022. 17(7). 347-353. doi: 10.22141/2224-0551.17.7.2022.1539.
- Melnik B.C., Stremmel W., Weiskirchen R. et al. Exosome-Derived MicroRNAs of Human Milk and Their Effects on Infant Health and Development. Biomolecules. 2021. 11. 851. doi: 10.3390/biom11060851.
- Van Herwijnen M.J.C., Driedonks T.A.P., Snoek B.L. et al. Abundantly Present miRNAs in Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Are Conserved Between Mammals. Front. Nutr. 2018 Sep 18. 5. 81. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00081.
- Golan-Gerstl R., Elbaum Shiff Y., Moshayoff V. et al. Cha–racterization and biological function of milk-derived miRNAs. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. 2017. 61(10). 1700009. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201700009.
- Smyczynska U., Bartlomiejczyk M.A., Stanczak M.M. et al. Impact of processing method on donated human breast milk microRNA content. PLoS One. 2020 Jul 15. 15(7). e0236126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236126.
- Tingö L., Ahlberg E., Johansson L. et al. Non-Coding RNAs in Human Breast Milk: A Systematic Review. Front. Immunol. 2021. 12. 725323. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.725323.
- Некротизуючий ентероколіт у передчасно народжених дітей. Клінічна настанова, заснована на доказах. Міністерство охорони здоров’я України. 2022.
- Duchon J., Barbian M.E., Denning P.W. Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Clin. Perinatol. 2021 Jun. 48(2). 229-250. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2021.03.002.
- Neu J. Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Future. Neonatology. 2020. 117(2). 240-244. doi: 10.1159/000506866.
- Thai J.D., Gregory K.E. Bioactive Factors in Human Breast Milk Attenuate Intestinal Inflammation during Early Life. Nutrients. 2020 Feb 23. 12(2). 581. doi: 10.3390/nu12020581.
- Meister A.L., Doheny K.K., Travagli R.A. Necrotizing enterocolitis: It’s not all in the gut. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood). 2020 Jan. 245(2). 85-95. doi: 10.1177/1535370219891971.
- Cho S.X., Rudloff I., Lao J.C. et al. Characterization of the pathoimmunology of necrotizing enterocolitis reveals novel therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Commun. 2020 Nov 13. 11(1). 5794. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19400-w.
- Li Y., Deng X., Zeng X., Peng X. The Role of Mir-148a in Cancer. J. Cancer. 2016 Jun 21. 7(10). 1233-41. doi: 10.7150/jca.14616.
- Chiba T., Kooka A., Kowatari K. et al. Expression profiles of hsa-miR-148a-3p and hsa-miR-125b-5p in human breast milk and infant formulae. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2022 Jan 3. 17(1). 1. doi: 10.1186/s13006-021-00436-7.
- Shiff Y.E., Reif S., Marom R. et al. MiRNA-320a is less expressed and miRNA-148a more expressed in preterm human milk compared to term human milk. Journal of Functional Foods. 2019. 57. 68-74.
- Chiba T., Takaguri A., Kooka A. et al. Suppression of milk-derived miR-148a caused by stress plays a role in the decrease in intestinal ZO-1 expression in infants. Clin. Nutr. 2022 Dec. 41(12). 2691-2698. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2022.10.004.
- Shah K.B., Chernausek S.D., Garman L.D. et al. Human Milk Exosomal MicroRNA: Associations with Maternal Overweight/Obesity and Infant Body Composition at 1 Month of Life. Nutrients. 2021 Mar 27. 13(4). 1091. doi: 10.3390/nu13041091.
- Frazier S., McBride M.W., Mulvana H., Graham D. From animal models to patients: the role of placental microRNAs, miR-210, –miR-126, and miR-148a/152 in preeclampsia. Clin. Sci. (Lond.). 2020 Apr 30. 134(8). 1001-1025. doi: 10.1042/CS20200023.
- Friedrich M., Pracht K., Mashreghi M.F. et al. The role of the miR-148/-152 family in physiology and disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017 Dec. 47(12). 2026-2038. doi: 10.1002/eji.201747132.
- Krishnachaitanya S.S., Liu M., Fujise K., Li Q. MicroRNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Its Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022 Aug 6. 23(15). 8751. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158751.
- Jiang K., Yang J., Yang C. et al. MiR-148a suppresses inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced endometritis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020 Jan. 24(1). 405-417. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14744.
- Li G., Tang X., Chen H. et al. MiR-148a inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines released by intervertebral disc cells by regulating the p38/MAPK pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018 Sep. 16(3). 2665-2669. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6516.
- Tang K., Wu Z., Sun M. et al. Elevated MMP10/13 mediated barrier disruption and NF-κB activation aggravate colitis and colon tumorigenesis in both individual or full miR-148/152 family knockout mice. Cancer Lett. 2022 Mar 31. 529. 53-69. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.12.033.
- Guo M.M., Zhang K., Zhang J.H. Human Breast Milk-Derived Exosomal miR-148a-3p Protects Against Necrotizing Enterocolitis by Regulating p53 and Sirtuin 1. Inflammation. 2022 Jun. 45(3). 1254-1268. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01618-5.
- Haftmann C., Stittrich A.B., Zimmermann J. et al. MiR-148a is upregulated by Twist1 and T-bet and promotes Th1-cell survival by regulating the proapoptotic gene Bim. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015 Apr. 45(4). 1192-205. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444633.