Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 18, №3, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Наукове обґрунтування підходів до фізичної реабілітації дітей із рецидивною бронхообструкцією
Авторы: I.A. Karimdzhanov, U.I. Zakirova, N.A. Israilova, N.B. Sodikova
Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Republic of Uzbekistan
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
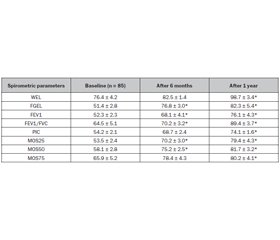
Актуальність. Основними завданнями лікування бронхолегеневих захворювань у дітей є контроль хвороби, досягнення стійкої ремісії, відновлення функції зовнішнього дихання, нервової системи, підвищення толерантності організму до дії алергенів. Кінезотерапія є одним з найефективніших методів немедикаментозної реабілітації. Метою нашого дослідження було патогенетичне обґрунтування застосування кінезогідротерапії методом контролю функції зовнішнього дихання на етапі реабілітації дітей із рецидивною бронхообструкцією. Результати. Порівняльний аналіз спірометричних показників у дітей із рецидивною бронхообструкцією до та після кінезогідротерапії в дослідній та контрольній групах показав ефективність методу комплексної реабілітації з включенням кінезогідротерапії зі спеціальною дихальною гімнастикою на суші та в басейні. Після річного реабілітаційного періоду порушення вентиляційної здатності легень за обструктивним типом зберігалися в легкій формі. У дітей із рецидивною бронхообструкцією, які неефективно застосовували фізичну реабілітацію з додатковими лікарськими рекомендаціями та фізіотерапією, як у дослідній групі, зберігаються порушення функції зовнішнього дихання у відновний період. Клінічно в дітей контрольної групи зберігалися часті рецидиви бронхообструкції на фоні гострих респіраторних захворювань. Отже, ці діти належать до групи із затяжним перебігом бронхообструкції та ризиком переходу в бронхіальну астму. Після курсу лікування значно порідшав кашель, нічних нападів не було, температура тіла стабільно нормалізувалася. При аускультації хрипів не вислуховується, дихання мало жорсткий відтінок. Висновки. Таким чином, використання комплексу лікувальних водних процедур і дихальної фізкультури, тобто кінезогідротерапії, є ефективним методом реабілітації дітей із рецидивною бронхообструкцією.
Background. The main objectives of the treatment of bronchopulmonary diseases in children are to control the disease, achieve a stable remission of the process, restore the function of external respiration, the nervous system, increase the body’s tolerance to the action of allergens. Kinesiotherapy is one of the most effective methods in non-drug rehabilitation. The purpose of our study was the pathogenetic justification of the use of kinesiohydrotherapy by the method of controlling the function of external respiration at the stage of rehabilitation of children with recurrent bronchial obstruction. Results. A comparative analysis of spirometric indicators in children with recurrent bronchial obstruction before and after kinesiohydrotherapy in the experimental and control groups showed the effectiveness of the method of comprehensive rehabilitation with the inclusion of kinesiohydrotherapy with special breathing exercises on land and in the pool. After a one-year rehabilitation period, violations of the ventilation capacity of the lungs by the obstructive type maintained in mild form. Сhildren with recurrent bronchial obstruction who did not effectively use physical rehabilitation with additional medical recommendations and physiotherapy as in experimental group, still had violations of the function of external respiration during the recovery period. Clinically, the children of control group continued to have frequent relapses of bronchial obstruction on the background of acute respiratory infections. Therefore, they belong to the group with a prolonged course of bronchial obstruction and the risk of transition to bronchial asthma. After the course of treatment, the cough became much less frequent, there were no night attacks, and the body temperature was steadily normal. Auscultation of wheezing was not heard, breathing had a harsh tinge. Conclusions. Thus, the use of therapeutic water procedures and respiratory physical exercises, i.e. kinesiohydrotherapy, is an effective method in the rehabilitation of children with recurrent bronchial obstruction.
бронхіт; обструкція; реабілітація; кінезотерапія; діти
bronchitis; obstruction; rehabilitation; kinesiotherapy; children
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Abaturov A.E., Rusakova O.O. Immunogenetic predictors of the development of bronchial obstruction during acute bronchitis in infants. Wiadomości Lekarskie. 2020. 73(2). 316-320.
- Абатуров А.Е., Волосовец А.П., Борисова Т.П. Медикаментозное управление окислительно-восстановительным состоянием организма при заболеваниях органов дыхания (часть 2). Здоров’я дитини. 2018. 3(13). 334-337. doi: 10.22141/2224-0551.13.3.2018.132918.
- Hamelmann E., von Mutius E., Bush A., Szefler S.J. Addres–sing the risk domain in the long-term management of pediatric asthma. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology. 2020. 31(3). 233-242. doi: 10.1111/pai.13175.
- Ibragimova M.F., Khusainova Sh.K., Rasulova N.A. Modern Concepts About Recurrent Bronchitis in Children (Literature Review). Eurasian Research Bulletin. 2022. 6. 18-21. Available from: https://www.geniusjournals.org/index.php/erb/article/view/738.
- Karimdjanov I.A., Zokirova U.I., Yusupova G.A., Karimova U.N. The role of association of ADRB2 gene polymorphism with therapeutic response to β2-agonists in children with recurrent bronchial obstruction. Child’s Health. 2022. 2(17). 19-23. doi: 10.22141/2224-0551.17.2.2022.1497.
- Lee E.G., Rhee C.K. Principles of asthma treatment and appropriate use of new drugs. Journal of the Korean Medical Association. 2022. 65. 44-54. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2022.65.1.44.
- Martin J., Townshend J., Brodlie M. Diagnosis and management of asthma in children. BMJ Paediatr. Open. 2022 Apr. 6(1). e001277. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2021-001277.
- Mirrakhimova M.Kh., Toshmatova G.A., Kurbanova D.R., Shamsiyeva E.R., Kasimova M.B., Abdullayeva M.M. Clinical efficacy of montelukast (L-Montus kid®) in the control of mild persistent bronchial asthma in children. Journal of Critical Reviews. 2020. 7(5). 805-807. doi: 10.31838/jcr.07.05.165.
- Morice A.H., Millqvist E., Bieksiene K., Birring S.S., Dicpinigaitis P., Ribas Ch.D., Boon M.H. et al. ERS guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of chronic cough in adults and children. European Respiratory Journal. 2020 Jan. 55(1). 1901136. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01136-2019.
- Teoibas-Serban D., Blendea C.D., Mihaltan F. Kinesiotherapy and physical activity in COPD and Asthma Patients — A Review. Balneo and PRM Research Journal. 2022. 13(2). 507-507.