Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 57, №3, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Значення остеопонтину у прогнозуванні фіброзу у пацієнтів з хронічним вірусним гепатитом С
Авторы: Шейко А.Г., Юрко К.В.
Харківський національний медичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
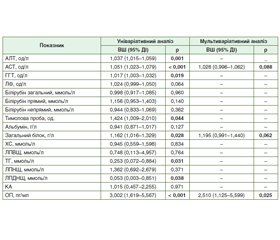
Актуальність. Діагностування безсимтомного перебігу хронічного вірусного гепатиту С (ХВГС) та наявного розвитку фіброзного процесу за допомогою визначення маркерних можливостей біохімічних показників крові (першочергово остеопонтину (ОП)) є актуальною проблемою сучасної медицини. Мета: встановити прогностичне значення біохімічних маркерів крові для діагностики безсимптомного перебігу ХВГС та наявного фіброзного процесу. Матеріали та методи. Обстежено 78 осіб: 47 основної групи (19 (40,4 %) жінок і 28 (59,6 %) чоловіків із ХВГС) і 31 — контрольної (відповідно 17 (54,8 %) і 14 (45,2 %) осіб жіночої та чоловічої статі без ХВГС). Розраховано медіану Me та 25% (LQ) і 75% (UQ) квартилі й відносні значення для кількісних та якісних показників відповідно. Визначення предикторів проводили за допомогою логістичного регресійного аналізу. Результати. Отримані за уніваріативним аналізом дані свідчать про вірогідно збільшені шанси на розвиток фіброзу печінки (ФП) на фоні ХВГС при підвищенні рівнів аланінамінотрансферази (АЛТ) в 1,037 раза і аспартатамінотрансферази (АСТ) в 1,051 раза; гамма-глутамілтрансферази (ГГТ) — в 1,017 раза; тимолової проби — в 1,424 раза; загального білка — в 1,162 раза та ОП — в 3,002 раза. При збільшенні тригліцеридів і ліпопротеїнів дуже низької щільності відзначено вірогідне зменшення таких шансів відповідно на 74,7 і 94,7 %. Використання мультиваріативного аналізу визначило вірогідно збільшені шанси на розвиток фіброзу печінки на фоні ХВГС при вищих рівнях АСТ, загального білка й ОП (відповідно в 1,028; 1,195 і 2,510 раза). Висновки. Визначено, що при значному ураженні печінки фіброзним процесом (3–4 стадія ФП) відзначається вірогідне переважання біохімічних печінкових маркерів крові хворих із ХВГС порівняно з 0–2 стадіями: АЛТ, АСТ, ГГТ, загального білка та ОП. Вірогідними предикторами прогнозування розвитку ФП визначені АСТ, загальний білок та ОП. Розроблена математична модель має високі показники чутливості та специфічності: відповідно 87,5 та 83,9 %.
Background. Diagnosis of an asymptomatic course of chronic viral hepatitis C (HCV) and the existing development of the fibrotic process by determining the marker capabilities of biochemical blood parameters (primarily osteopontin — OP) is an urgent issue in modern medicine. Purpose: to evaluate the prognostic value of biochemical blood markers for diagnosing an asymptomatic course of HCV and the existing fibrotic process. Materials and methods. Seventy-eight people were examined: 47 from the main group — 19 (40.4 %) women and 28 (59.6 %) men with chronic HCV, and 31 controls — 17 (54.8 %) women and 14 (45.2 %) men without chronic HCV. The median, as well as 25.0% and 75.0% quartiles and relative values were calculated for quantitative and qualitative measures, respectively. Predictors were determined using logistic regression analysis. Results. The data obtained by a univariate analysis indicate a significantly increased risk of developing liver fibrosis on the background of chronic HCV, with alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels increased by 1.037 times, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) by 1.051 times, gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) by 1.017 times; thymol turbidity test by 1.424 times; total protein by 1.162 times and OP by 3.002 times. With increased levels of triglycerides and very low-density lipoproteins, a significant decrease in these risks was found, by 74.7 and 94.7 %, respectively. A multivariate analysis found significantly increased risks of developing liver fibrosis on the background of chronic HCV, with higher levels of AST, total protein, and OP (by 1.028, 1.195 and 2.510 times, respectively). Conclusions. With a significant liver damage by a fibrotic process (stage 3–4), as compared to stage 0–2, there is a probable predominance of biochemical liver markers in the blood of patients with HCV: ALT, AST, GGT, total protein and OP. AST, total protein, and OP were identified as reliable predictors of liver fibrosis. The developed mathematical model has high sensitivity and specificity: 87.5 and 83.9 %, respectively.
остеопонтин; фіброз печінки; хронічний вірусний гепатит С; прогностичне значення
osteopontin; liver fibrosis; chronic viral hepatitis C; prognostic significance
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Epidemiology and natural history of hepatitis C virus infection among children and young people / L. Modin et al. J Hepatol. 2019. Vol. 70 (3). P. 371-378. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.11.013.
- The Hepatitis C Virus Care Continuum: Linkage to Hepatitis C Virus Care and Treatment Among Patients at an Urban Health Network, Philadelphia, PA / C. Coyle et al. Hepatology. 2019. Vol. 70 (2). P. 476-486. doi: 10.1002/hep.30501.
- Do A., Reau N.S. Chronic Viral Hepatitis: Current Management and Future Directions. Hepatol Commun. 2020. Vol. 4 (3). Р. 329-341. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1480.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu; Clinical Practice Guidelines Panel: Chair; EASL Governing Board representative; Panel members: EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C: Final update of the series. J He–patol. 2020. Vol. 73 (5). P. 1170-1218. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.08.018.
- Viral Hepatitis C Therapy: Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations: A 2019 Update / E.J. Smolders et al. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. Vol. 58 (10). P. 1237-1263. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00774-0.
- Vitamin D derivatives inhibit hepatitis C virus production through the suppression of apolipoprotein / A. Murayama et al. Antiviral Res. 2018. Vol. 160. P. 55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.10.014.
- ACHIEVE Coalition. Many European countries 'flying blind' in their efforts to eliminate viral hepatitis / J.V. Lazarus et al. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. Vol. 26. № 14 (8). P. 445-446. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.98.
- World Health Organization. Global hepatitis report. 2017. URL: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c.
- Significance of biglycan and osteopontin as non-invasive mar–kers of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus and chronic hepatitis C virus / A. Sobhy et al. J Investig Med. 2019. Vоl. 67 (3). P. 681-685. doi: 10.1136/jim-2018-000840.
- Osteopontin versus alpha-fetoprotein as a diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis / T. Sun et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. Vol. 11. P. 8925-8935. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S186230.
- Serum osteopontin predicts degree of hepatic fibrosis and serves as a biomarker in patients with hepatitis C virus infection / Y. Matsue et al. PLoS One. 2015. Vol. 10 (3). e0118744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118744.
- Osteopontin is up-regulated in chronic hepatitis C and is associated with cellular permissiveness for hepatitis C virus replication / S.S. Choi et al. Clinical Science. 2014. Vol. 126 (12). P. 845-855. doi: https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20130473.
- Infection with Hepatitis B Virus May Increase the Serum Concentrations of Osteopontin / H.B. Liu et al. Intervirology. 2021. Vol. 64 (3). P. 126-134. doi: 10.1159/000513687.
- The osteopontin-CD44 axis in hepatic cancer stem cells regulates IFN signaling and HCV replication / T. Shirasaki et al. Sci Rep. 2018. № 8 (1). P. 13143. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31421-6.
- Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 and Osteopontin Serum Le–vels as Biomarkers for Biliary Atresia / B. Aldeiri et al. J Pe–diatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2023. № 77 (1). P. 97-102. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000003792.