Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 18, №8, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Оцінка ефективності надання медичної допомоги дітям, хворим на цукровий діабет, у різних областях України протягом останніх 20 років (2002–2021 рр.) мирного час
Авторы: Мітюряєва-Корнійко І.О., Волосовець О.П., Кривопустов С.П., Полухіна М.О., Бурлака Є.А., Кривонос Ю.М., Ковальчук І.В.
Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
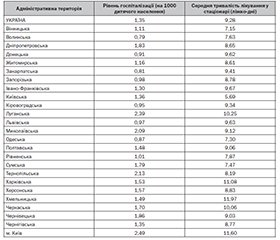
Актуальність. Зростаюча кількість дітей з цукровим діабетом (ЦД) створює глобальну економічну проблему в галузі охорони здоров’я, зокрема фінансовий тягар для системи охорони здоров’я країни та економічний стрес для сімей дітей, хворих на ЦД. Мета дослідження. Оцінити показники ефективності надання медичної допомоги дітям, хворим на цукровий діабет, різних регіонів України протягом останніх 20 років (2002–2021 рр.) мирного часу. Матеріали та методи. У статті наведені результати статистичної оцінки та епідеміологічного аналізу даних Центру медичної статистики МОЗ України щодо показників інвалідності, рівня госпіталізації, показників надання стаціонарної допомоги серед дитячого населення протягом 2002–2021 років. Статистична обробка результатів проводилася за допомогою програми MS Excel, XLSTAT-Pro. Результати. Протягом 2002–2021 років найшвидшими темпами зростає показник первинної інвалідності внаслідок ЦД серед групи підлітків — у 4,1 раза; найменшими — у дітей молодшого шкільного віку — у 3,4 раза, а серед дітей 0–6 років — у 3,6 раза. Питома вага дітей-інвалідів унаслідок ЦД станом на 2017 рік становить 12 % серед вікової групи 0–6 років, 25 % — серед підлітків (15–17 років). Протягом 2013–2021 рр. рівень госпіталізації дітей, хворих на ЦД, збільшився з 1,27 до 1,35 на 1000 відповідного населення, а показник середньої тривалості лікування у стаціонарі зменшився на 19 %. Показник летальності від ускладнень цукрового діабету серед госпіталізованих дітей коливається та не має чіткої тенденції (у 2021 році становив 0,02 на 100 госпіталізованих). Висновки. Аналіз ефективності надання медичної допомоги дітям, хворим на ЦД, протягом 2002–2021 рр. в умовах зростання поширеності та захворюваності на ЦД показав стійкі тенденції: до колосального зростання рівня первинної та загальної інвалідності, незначного підвищення рівня госпіталізації, зменшення середньої тривалості лікування у стаціонарі. Отримані результати свідчать про необхідність детального вивчення причин, контролю та перегляду протокольних документів ведення таких хворих.
Background. The growing number of children with diabetes creates a global economic problem, including a financial burden on the country’s health care system and economic stress for families of children with diabetes. The purpose was to assess the effectiveness of medical care for children with diabetes in different regions of Ukraine over the last 20 years (2002–2021) of peacetime. Material and methods. The article presents the results of statistical evaluation and epidemiological analysis of data from the Center for Medical Statistics of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine on the rates of disability, hospitalization, and inpatient care among the pediatric population in 2002–2021. Statistical processing of the results was carried out using MS Excel, XLSTAT-Pro. Results. During 2002–2021, an increase in the rate of primary disability due to diabetes mellitus was highest among adolescents — by 4.1 times and lowest among primary schoolchildren — by 3.4 times; among children 0–6 years old, it increased by 3.6 times. The proportion of children with disabilities due to diabetes as of 2017 is 12 % among the age group of 0–6 years, and 25 % in adolescents (15–17 years). In 2013–2021, the hospitalization rate among children with diabetes increased from 1.27 to 1.35 per 1,000 of the relevant population, and the average length of hospital stay decreased by 19 %. The rate of mortality due to diabetes complications among hospitalized children varies and does not have a specific trend (in 2021, it was 0.02 per 100 in-patients). Conclusions. The analysis of the efficiency of medical care for children with diabetes during 2002–2021 in the context of increasing prevalence and incidence of diabetes showed stable trends towards a huge increase in the level of primary and general disability, a slight increase in hospitalization rates, and a decrease in the average length of hospital stay. These results call for a detailed study of the causes, control, and revision of protocol documents for the management of such patients.
діти; цукровий діабет; інвалідність; госпіталізація; смертність
children; diabetes mellitus; disability; hospitalization; mortality
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- James Maniam J., Cheung P.-T., Urakami T., von Oettingen J., Likitmaskul S. Epidemiology and phenotypes of diabetes in children and adolescents in non-European-origin populations in or from Western Pacific region. World Journal of Clinical Pediatrics. 2022. 11(2). 173-195. https://dx.doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v11.i2.173.
- Patterson C.C., Karuranga S., Salpea P., Saeedi P., Dahlquist G., Soltesz G., Ogle G.D. Worldwide estimates of incidence, prevalence and mortality of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Research аnd Clinical Practice. 2019. 157. 107842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107842.
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th Edition. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation, 2021.
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Tech. Rep., International Diabetes Federation, Brussels, Belgium, 2019.
- Lawrence J.M., Divers J., Isom S., et al. Trends in prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in the US, 2001-2017. JAMA. 2021. 326(8). 717-727.
- Mayer-Davis E.J., Lawrence J.M., Dabelea D., et al. Incidence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among youths, 2002-2012. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017. 376(15). 1419-1429.
- Maahs D.M., West N.A., Lawrence J.M., Mayer-Davis E.J. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America. 2010. 39(3). 481-497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2010.05.011.
- SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group, Liese A.D., D’Agostino R.B., Jr, Hamman R.F., Kilgo P.D., Lawrence J.M., Liu L.L., et al. The burden of diabetes mellitus among US youth: prevalence estimates from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Pediatrics. 2006. 118(4). 1510-1518. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2006-0690.
- Gregg E.W., Menke A. Diabetes and Disability. In: Cowie C.C., Casagrande S.S., Menke A., Cissell M.A., Eberhardt M.S., Meigs J.B., et al., editors. Diabetes in America. 3rd ed. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (US); 2018 Aug. CHAPTER 34. URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567983/
- The Economic Burden of Hospital Costs on Families With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Children: The Role of Medical Insurance in Shandong Province, China. S. Wang, Y. Guo, E. Maitland, S. Nicholas, J. Sun, A. Leng. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.853306.
- Streisand R., Monaghan M. Young children with type 1 diabetes: challenges, research, and future directions. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2014. 14(9). 520. doi: 10.1007/s11892-014-0520-2. PMID: 25009119; PMCID: PMC4113115.
- Будрейко О.А., Кирилова О.О., Чумак С.О. Комплексна оцінка мотивації до самоконтролю у підлітків із цукровим діабетом 1 типу. Методичні рекомендації. Український журнал дитячої ендокринології. 2018. № 2. С. 75-84. Режим доступу: http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/ujde_2018_2_11.
- ДЗ «Центр медичної статистики МОЗ України», м. Київ. URL: http://medstat.gov.ua/ukr/main.html.
- de Villiers F.P., Chester E., Meyers K.E. Blood glucose control and compliance of diabetic children. Curationis. 1997 Jul. 20(2). 12-6. doi: 10.4102/curationis.v20i2.1299. PMID: 9418408.
- Settineri S., Frisone F., Merlo E.M., Geraci D., Martino G. Compliance, adherence, concordance, empowerment, and self-management: five words to manifest a relational maladjustment in diabetes. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2019 Apr 29. 12. 299-314. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S193752. PMID: 31118655; PMCID: PMC6499139.
- Couch R., Jetha M., Dryden D.M., Hooten N., Liang Y., Durec T., et al. Diabetes education for children with type 1 diabetes mellitus and their families. Evid. Re.p Technol. Assess. (Full Rep.). 2008 Apr. (166). 1-144. PMID: 18620470; PMCID: PMC4781150.