Журнал «Боль. Суставы. Позвоночник» Том 14, №2, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Ефективність використання біоактивного концентрату морської риби в пацієнтів з болем у спині
Авторы: Орос М.М. (1), Фістер Н.І. (1), Акімов О.Є. (2), Костенко В.О. (2)
(1) - ДВНЗ «Ужгородський національний університет», м. Ужгород, Україна
(2) - Полтавський державний медичний університет, м. Полтава, Україна
Рубрики: Ревматология, Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
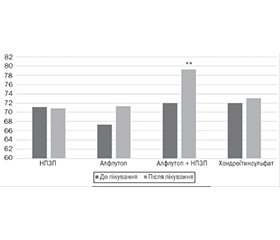
Актуальність. Біль у спині — поширена медична проблема, що має значні медико-соціальні наслідки. З огляду на актуальність проблеми й необхідність оцінки найбільш ефективного методу купірування больового синдрому і поліпшення стану пацієнтів з урахуванням можливої токсичності й індивідуальної непереносимості певного типу ліків важливим є дослідження та порівняння різних підходів, а саме лікарських засобів різної дії та їх комбінування. Мета: дослідити ефективність застосування біоактивного концентрату морської риби (БКМР) і його комбінації з нестероїдним протизапальним препаратом (НПЗП) у лікуванні болю в спині порівняно з терапією монокомпонентним хондроїтинсульфатом (ХС) натрію в лікарській формі для перорального застосування. Матеріали та методи. Обстежено чотири групи пацієнтів, кожна з яких складалась з 30 осіб чоловічої або жіночої статі зі скаргами на біль у спині. Кожній групі призначали один з трьох лікарських засобів — НПЗП у стандартному дозуванні, ХС натрію у дозі 1 г/д (2 капсули по 500 мг) і БКМР у вигляді внутрішньом’язових ін’єкцій у дозі 1 мл/д (0,2 мл). 4-та група пацієнтів отримувала комбіноване лікування, а саме 1 мл/д БКМР і НПЗП у стандартному дозуванні. Пацієнтам, які взяли участь у дослідженні, було проведено лабораторні й інструментальні обстеження. Результати. Застосування БКМР і його комбінації з НПЗП супроводжувалося кращою суб’єктивною оцінкою пацієнтами власного психоемоційного стану, пов’язаного зі зниженням інтенсивності болю в спині, зростанням показників якості життя і зменшенням вираженості тривоги й депресії. Комбінація БКМР з НПЗП виявляла більш виражений ефект щодо зниження рівня фактора некрозу пухлини α у крові, ніж монотерапія БКМР. Показано також позитивний вплив комбінованої терапії на стан судин нижніх кінцівок за даними доплерографії. Висновки. БКМР може бути ефективним доповненням до стандартної терапії болю в спині.
Background. The urgency of pain relief and patient improvement necessitates evaluating the most effective treatment approaches. This includes a comparative analysis of medications with different mechanisms of action, both taken individually and in combination while considering potential drug toxicity and individual patient intolerances. The study purposed to assess the efficacy of a bioactive concentrate derived from marine fish (BCMF), both alone and in combination with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), for the treatment of back pain, in comparison to therapy involving solely oral sodium chondroitin sulfate (CS). Materials and methods. We examined four groups of patients, each comprising 30 male or female subjects with complaints of back pain. Each group was administered one of three medications: NSAIDs in a standard dosage, CS in a daily dose of 1 g (two capsules of 500 mg each), and BCMF in the form of intramuscular injections in a daily dose of 1 ml (0.2 ml per injection). The fourth group of patients received combined treatment, namely, 1 ml of BCMF and NSAIDs in a standard dosage daily. All participants underwent laboratory tests and instrumental examinations. Results. The administration of BCMF, both alone and in combination with NSAIDs resulted in an improved subjective assessment of patients’ psychoemotional well-being, marked by reduced back pain intensity, enhanced quality of life indices, and diminished levels of anxiety and depression. The combination of BCMF with NSAIDs demonstrated a more pronounced effect on reducing tumor necrosis factor α serum concentration than monotherapy with BCMF. The combination therapy positively impacted the condition of lower extremity vessels as indicated by Doppler ultrasonography. Conclusions. BCMF can be an effective addition to the standard therapy of back pain.
біль у спині; біоактивний концентрат морської риби; хондроїтинсульфат; нестероїдні протизапальні препарати; системна запальна відповідь; психоемоційний стан; шкала якості життя
back pain; bioactive concentrate of marine fish; chondroitin sulfate; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; systemic inflammatory response; psychoemotional state; quality of life
scale