Журнал «Боль. Суставы. Позвоночник» Том 15, №3, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Вплив терапії кальциміметиками на мінерально-кісткові розлади у хворих на хронічну хворобу нирок VД стадії
Авторы: Мартинюк Л.П. , Мальська Т.Л.
ДВНЗ «Тернопільський національний медичний університет ім. І.Я. Горбачевського МОЗ України», м. Тернопіль, Україна
Рубрики: Ревматология, Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
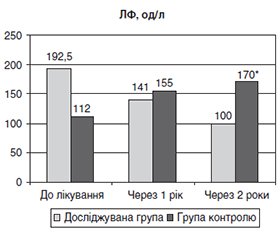
Актуальність. Вивчення особливостей перебігу вторинного гіперпаратиреозу (ВГПТ) та його лікування у пацієнтів з хронічною хворобою нирок (ХХН) VД стадії є актуальною проблемою. Мета: вивчити вплив довготривалої комплексної терапії (ДКТ) з включенням кальциміметика цинакальцету на перебіг ВГПТ у хворих з ХХН VД стадії. Матеріали та методи. В одноцентровому когортному проспективному дослідженні обстежено 134 особи з ХХН VД стадії, які отримували нирково-замісну терапію програмним гемодіалізом. Досліджувана група включала хворих, які отримували ДКТ та базову терапію ВГПТ із застосуванням вітаміну D (альфакальцидолу) і кальційвмісного/синтетичного фосфатбіндера ацетату кальцію/севеламеру гідрохлориду; група контролю отримувала довготривалу базову терапію. У всіх хворих визначали рівні інтактного паратгормону (іПТГ), сироваткового кальцію (Са) та фосфору (Р), активність лужної фосфатази (ЛФ) до лікування й на тлі терапії через один і два роки. Аналіз отриманих даних проведено з використанням програми SPSS, версії 21 із статистичною значимістю, визначеною на рівні p < 0,05. Результати. ВГПТ виявлено у 33,6 % пацієнтів із ХХН VД стадії, середній вік яких становив 52,2 ± 12,9 року. Довготривале застосування цинакальцету сприяло досягненню цільового рівня іПТГ у 83,3 % пацієнтів з ВГПТ, що супроводжувалося вірогідним зниженням у них частоти переломів та клінічно значущої кальцифікації судин. На тлі ДКТ з включенням цинакальцету мало місце також вірогідне зниження рівня Р, Са та меншою мірою активності ЛФ у пацієнтів з ВГПТ. Висновки. При довготривалій терапії із включенням цинакальцету мало місце вірогідне зниження рівня іПТГ, що супроводжувалося зниженням рівня сироваткового Р, Са та ЛФ, а також вірогідним зниженням частоти переломів і кальцифікації судин. Цинакальцет можна розцінювати як безпечний та ефективний засіб у лікуванні ВГПТ у пацієнтів з ХХН VД стадії.
Background. Determination of peculiarities of the secondary hyperparathyroidism’s course (sHPT) and its treatment in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) G5D is an actual problem. The purpose was to study the effect of long-term therapy with the inclusion of the calcimimetic cinacalcet (LСT) on the course of sHPT in CKD G5D patients. Materials and methods. In the single-center cohort prospective study we examined 134 personss with CKD G5D, who received therapy by program hemodialysis. The study group included patients who received LСT and basic sHPT therapy with the use of vitamin D (alfacalcidol) and calcium-containing/synthetic phosphate-binder calcium acetate/sevelamer hydrochloride; the control group received long-term basic therapy. In all patients, levels of intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH), serum calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity were determined before treatment, after one and after two years of therapy. The data were analyzed using SPSS, version 21, with statistical significance set at p <0.05. Results. SHPT was detected in 33.6 % of patients, whose average age was 52.2 ± 12.9 years. LCT contributed to the achievement of the target level of iPTH in 83.3 % of patients with sHPT, which was accompanied by a significant decrease in the frequency of fractures and clinically significant vascular calcification. During LCT there was also significant decrease of P, Ca level and, to a lesser extent, ALP activity in patients with sHPT. Conclusion. During LCT of sHPT with cinacalcet, there was a significant decrease in the level of iPTH, which was accompanied by a decrease in the level of serum P, Ca and, to a lesser extent, ALP. Cinacalcet can be considered as a safe and effective tool in the treatment of sHPT in CKD G5D patients.
вторинний гіперпаратиреоз; гемодіаліз; паратиреоїдний гормон; мінеральні та кісткові розлади; кальциміметики
secondary hyperparathyroidism; hemodialysis; parathyroid hormone; mineral and bone disorders; calcimimetics
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Jadoul M, Aoun M, Masimango Imani M. The major global burden of chronic kidney disease. Lancet Glob Health. 2024 Mar;12(3):e342-e343. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(24)00050-0.
- Hedgeman E, Lipworth L, Lowe K, Saran R, Do T, Fryzek J. International burden of chronic kidney disease and secondary hyperparathyroidism: a systematic review of the literature and available data. Int J Nephrol. 2015;2015:184321. doi: 10.1155/2015/184321.
- Tabibzadeh N, Karaboyas A, Robinson BM, et al. The risk of medically uncontrolled secondary hyperparathyroidism depends on parathyroid hormone levels at haemodialysis initiation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021 Jan 1;36(1):160-169. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa195.
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Update Work Group. KDIGO 2017 Clinical Practice Guideline Update for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2017 Jul;7(1):1-59. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2017.04.001.
- Muhetaer G, Liu G, Zhang L, Jiang H. Severe secondary hyperparathyroidism in a chronic kidney disease patient treated with Radiofrequency ablation: One case report. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 22;9:876692. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.876692.
- Habas E Sr, Eledrisi M, Khan F, Elzouki AY. Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiology and Management. Cureus. 2021 Jul 14;13(7):e16388. doi: 10.7759/cureus.16388.
- Torres PU. Cinacalcet HCl: a novel treatment for secondary hyperparathyroidism caused by chronic kidney disease. J Ren Nutr. 2006 Jul;16(3):253-258. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2006.04.010.
- Reiss AB, Miyawaki N, Moon J, et al. CKD, arterial calcification, atherosclerosis and bone health: Inter-relationships and controversies. Atherosclerosis. 2018 Nov;278:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.08.046.
- Galassi A, Ciceri P, Fasulo E, Carugo S, Cianciolo G, Cozzolino M. Management of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Focus on the Elderly. Drugs Aging. 2019 Oct;36(10):885-895. doi: 10.1007/s40266-019-00696-3.
- Hiramitsu T, Hasegawa Y, Futamura K, et al. Treatment for secondary hyperparathyroidism focusing on parathyroidectomy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 20;14:1169793. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1169793.
- Harris RZ, Padhi D, Marbury TC, Noveck RJ, Salfi M, Sullivan JT. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of cinacalcet hydrochloride in hemodialysis patients at doses up to 200 mg once daily. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004 Dec;44(6):1070-1076. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2004.08.029.
- Nemeth EF, Heaton WH, Miller M, et al. Pharmacodynamics of the type II calcimimetic compound cinacalcet HCl. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Feb;308(2):627-635. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.057273.
- Lindberg JS, Culleton B, Wong G, et al. Cinacalcet HCl, an oral calcimimetic agent for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis: a randomized, double-blind, multicenter study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Mar;16(3):800-807. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004060512.
- Xu J, Yang Y, Ma L, Fu P, Peng H. Cinacalcet plus vitamin D versus vitamin D alone for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients undergoing dialysis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019 Nov;51(11):2027-2036. doi: 10.1007/s11255-019-02271-6.
- Lozano-Ortega G, Waser N, Bensink ME, et al. Effects of calcimimetics on long-term outcomes in dialysis patients: literature review and Bayesian meta-analysis. J Comp Eff Res. 2018 Jul;7(7):693-707. doi: 10.2217/cer-2018-0015.
- Kawata T, Nagano N, Obi M, et al. Cinacalcet suppresses calcification of the aorta and heart in uremic rats. Kidney Int. 2008 Nov;74(10):1270-1277. doi: 10.1038/ki.2008.407.
- Cunningham J, Danese M, Olson K, Klassen P, Chertow GM. Effects of the calcimimetic cinacalcet HCl on cardiovascular disease, fracture, and health-related quality of life in secondary hyperparathyroidism. Kidney Int. 2005 Oct;68(4):1793-800. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00596.x.
- Haarhaus M, Cianciolo G, Barbuto S, et al. Alkaline Phosphatase: An Old Friend as Treatment Target for Cardiovascular and Mineral Bone Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients. 2022 May 19;14(10):2124. doi: 10.3390/nu14102124.
- Tahara H. Role of cinacalcet in management of mineral bone disorder in chronic kidney disease (control of calcium, phosphorus and parathyroid hormone). Ther Apher Dial. 2008 Oct;12(Suppl 1):S27-S33. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-9987.2008.00628.x.
- Chertow GM, Correa-Rotter R, Block GA, et al. Baseline characteristics of subjects enrolled in the Evaluation of Cinacalcet HCl Therapy to Lower Cardiovascular Events (EVOLVE) trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Jul;27(7):2872-2879. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr777.
- Ureña-Torres P, Bridges I, Christiano C, et al. Efficacy of cinacalcet with low-dose vitamin D in incident haemodialysis subjects with secondary hyperparathyroidism. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 May;28(5):1241-1254. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs568.